State-Specific Assisted Reproductive Technology Surveillance
In 2019, 2.1% of all infants born in the United States (includes the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico) were conceived with the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART). ART is defined as fertility treatments where eggs or embryos are handled for the purpose of establishing a pregnancy. The most common type of ART is in vitro fertilization (IVF). Although ART-conceived infants account for a small proportion of all infants born, ART contributed to 10.6% of all multiples (twins, triplets, etc.) born in the United States.
Use of ART, embryo transfer practices, and outcomes of ART-conceived births vary by state (or territory). For example, in 2019, the proportion of ART-conceived infants among all infants ranged from 0.5% in Puerto Rico to 5.5% in Massachusetts, and rates of ART-conceived multiples ranged from 8.6% in Delaware to 37.3% in North Dakota. State-based ART surveillance is vital for monitoring variations among states (or territories) in ART use, practice, and outcomes such as rates of multiple birth and prematurity. State-specific data can help stakeholders develop risk-reduction interventions related to ART. CDC annually publishes a state-specific surveillance summary using data from National ART Surveillance System (NASS) and National Vital Statistics System (NVSS) as data become available.
Assisted Reproductive Technology Clinics
In 2019, a total of 489 fertility clinics in the United States performed ART procedures and 448 (91.6%) provided data to CDC. The number of fertility clinics performing ART procedures varied by state (or territory). The states with the largest numbers of fertility clinics providing data were California (72), New York (43), and Texas (42).
Number of ART clinics—United States, 2019
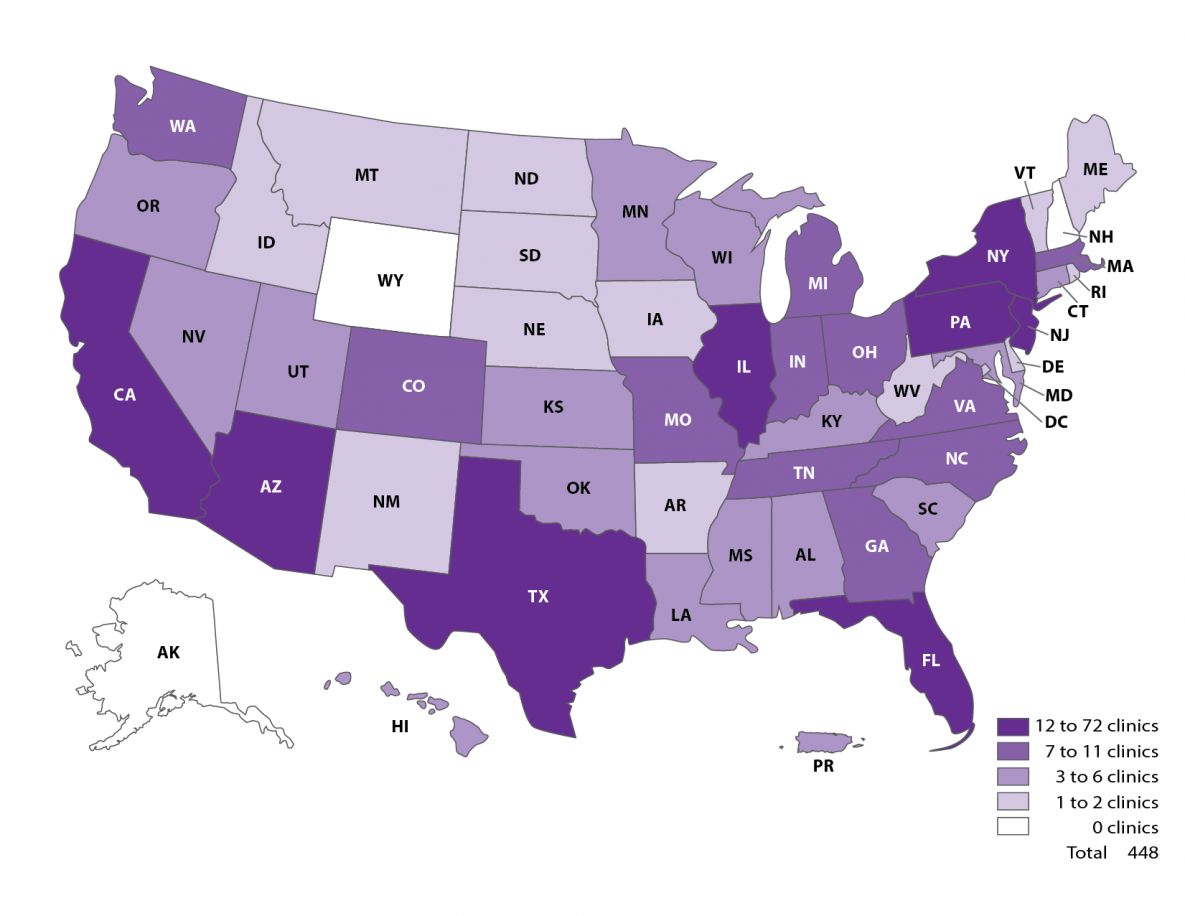
Assisted Reproductive Technology Use
Two measures of ART use are 1) the proportion of ART infants among all infants born in a particular state (or territory) and 2) the number of ART procedures performed per 1 million women of reproductive age (15 to 44 years) in a state (or territory). In 2019, both measures of ART use showed substantial variations by state (or territory) in the United States.
Proportion of ART infants among all infants born, 2019
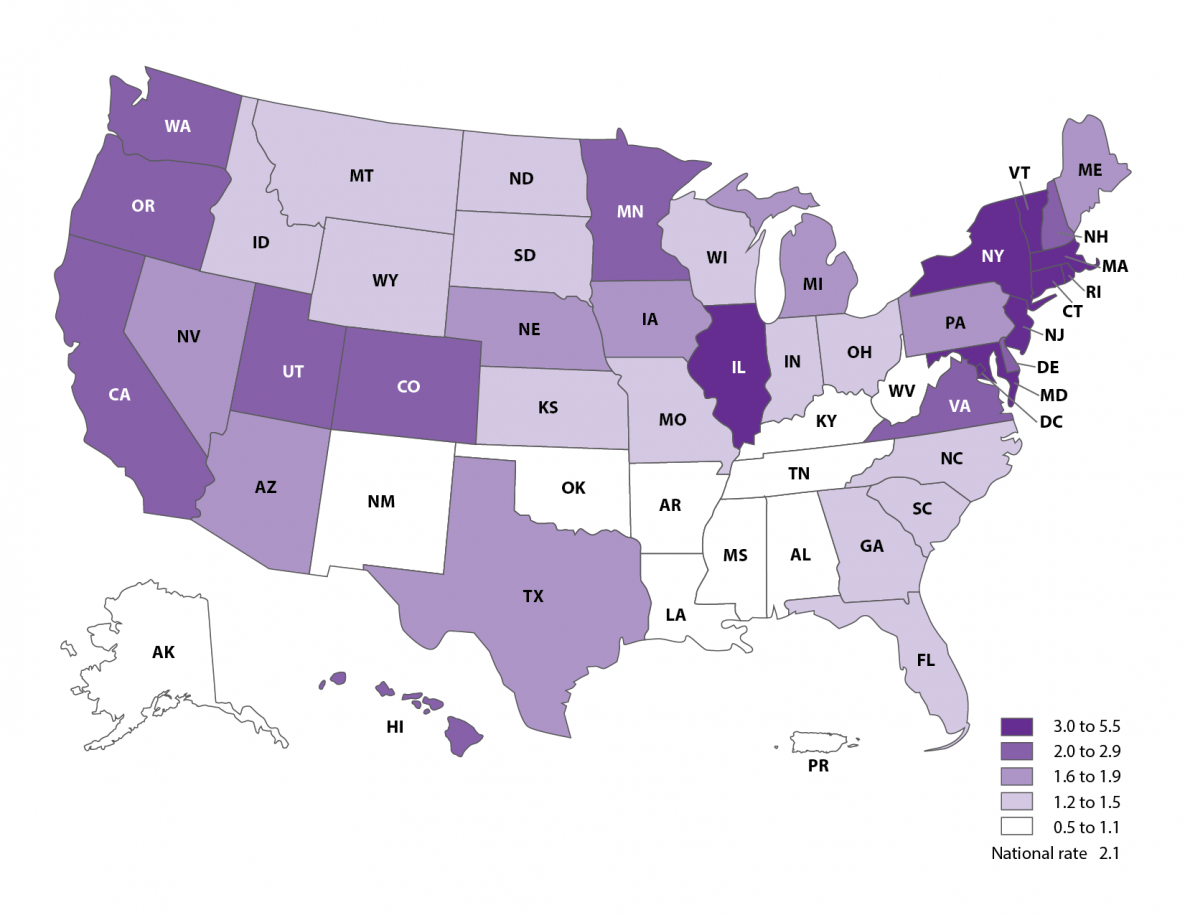
- Nationally, ART accounted for 2.1% of all infants born in the United States.
- The proportion of ART use among all infants born was highest in Massachusetts (5.5%), the District of Columbia (5.0%), and New Jersey (4.4%).
- The proportion of ART use among all infants born was lowest in Puerto Rico (0.5%), Arkansas (0.6%), and Alabama (0.7%).
ART procedures performed per 1 million women aged 15-44 years, 2019
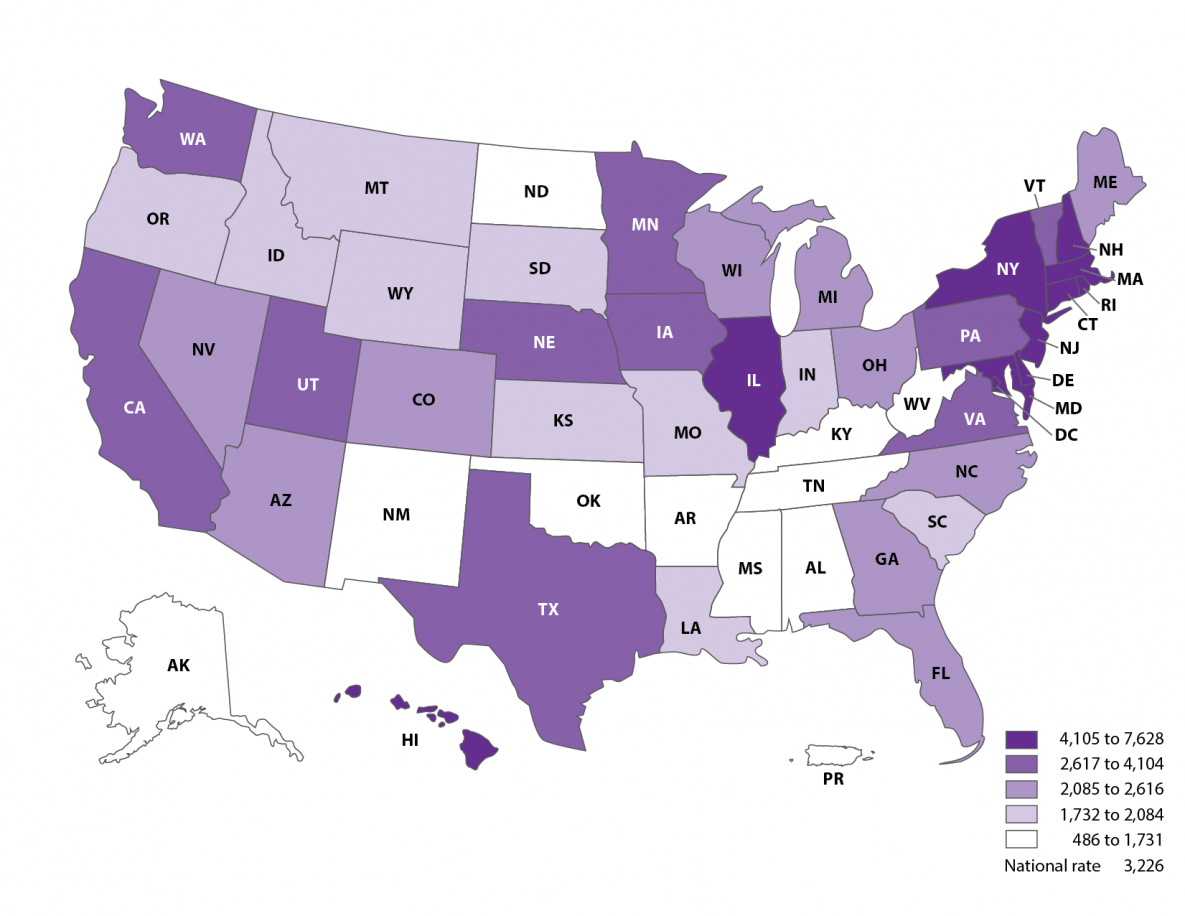
- The national rate of ART use was 3,226 procedures performed per 1 million women of reproductive age (15 to 44 years).
- Sixteen states—California, Connecticut, Delaware, the District of Columbia, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Utah, Vermont and Virginia, had ART use rates higher than the national rate.
- Two states—Massachusetts and the District of Columbia had ART use rates exceeding twice the national level.
- Some states have passed insurance mandates requiring private insurers to cover at least two ART treatment cycles. This type of mandated insurance coverage has been associated with greater use of ART and may explain some of the differences in ART use among states.
Assisted Reproductive Technology Practice
Women who undergo ART procedures are more likely to have multiple-birth deliveries than women who conceive naturally. This is because more than one embryo may be transferred during an ART procedure. Guidelines issued by American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) and Society of Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) in 2017 focused on promoting single-embryo transfer (SET) where medically feasible for all favorable prognosis patients who are most likely to be women younger than 35 years. Rates of SET procedures (transfer of one embryo) in the United States varied among states (or territories). Below are SET rates among women younger than 35 years.
Single embryo transfer rates among women <35 years, 2019
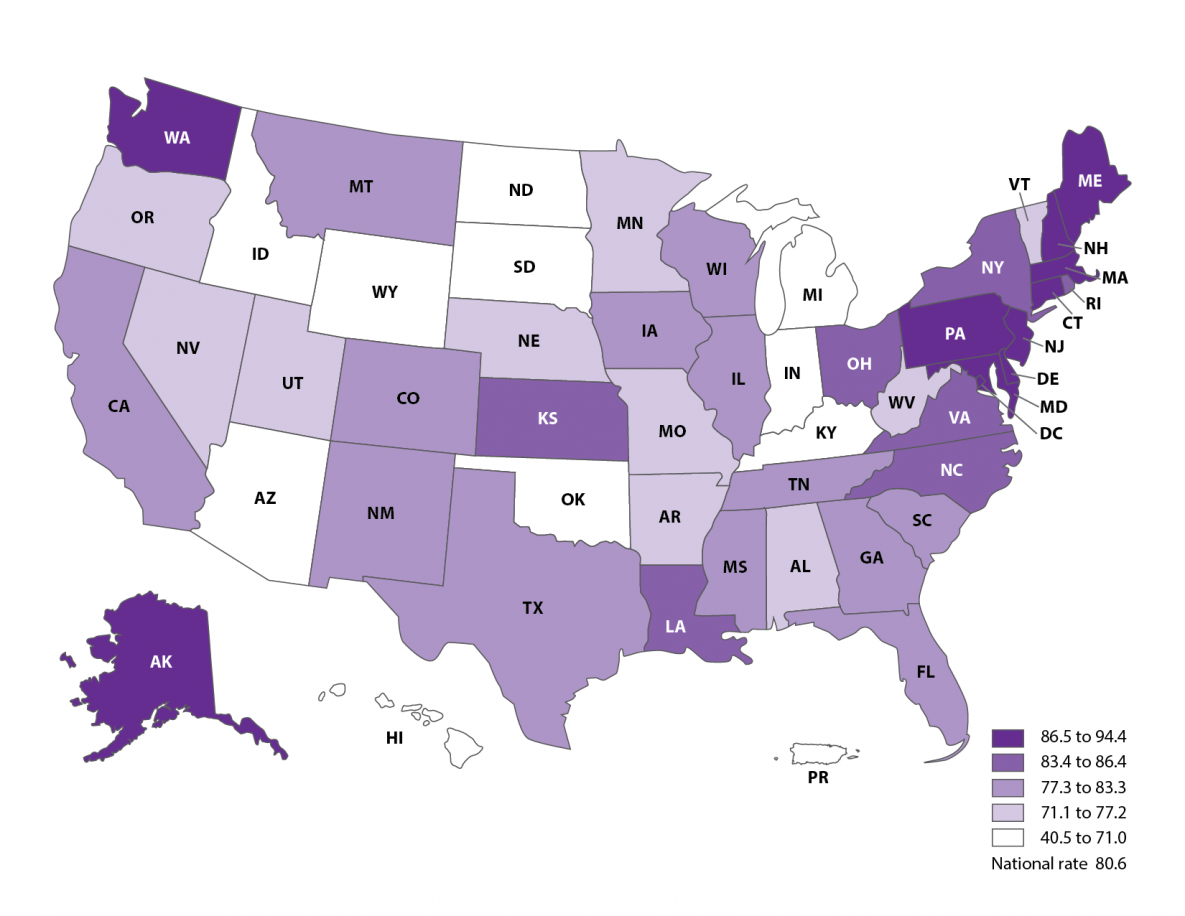
- Nationally, SET rate among women younger than 35 years was 80.6%.
- The highest SET rates among women younger than 35 years were observed in the District of Columbia (94.4%), Delaware (93.0%), and Maryland (90.3%).
- The lowest SET rates among women younger than 35 years were observed in the Michigan (56.4%), South Dakota (51.7%), and Puerto Rico (40.5%).
Multiple-Birth Rates
ART infants were less likely to be singletons (83.2%), and more likely to be multiples- twins, triplets, etc. (16.8%) compared with all infants born in the general population (96.7% and 3.3%, respectively). A substantial proportion (97.0%) of ART-conceived multiples were twins, and a smaller proportion (3.0%) were triplets and higher-order infants. Nationally, ART contributed to 10.6% of all multiples born in the United States, even though ART infants accounted for only 2.1% of all infants born in the United States.
Percentage of multiples among ART infants, 2019
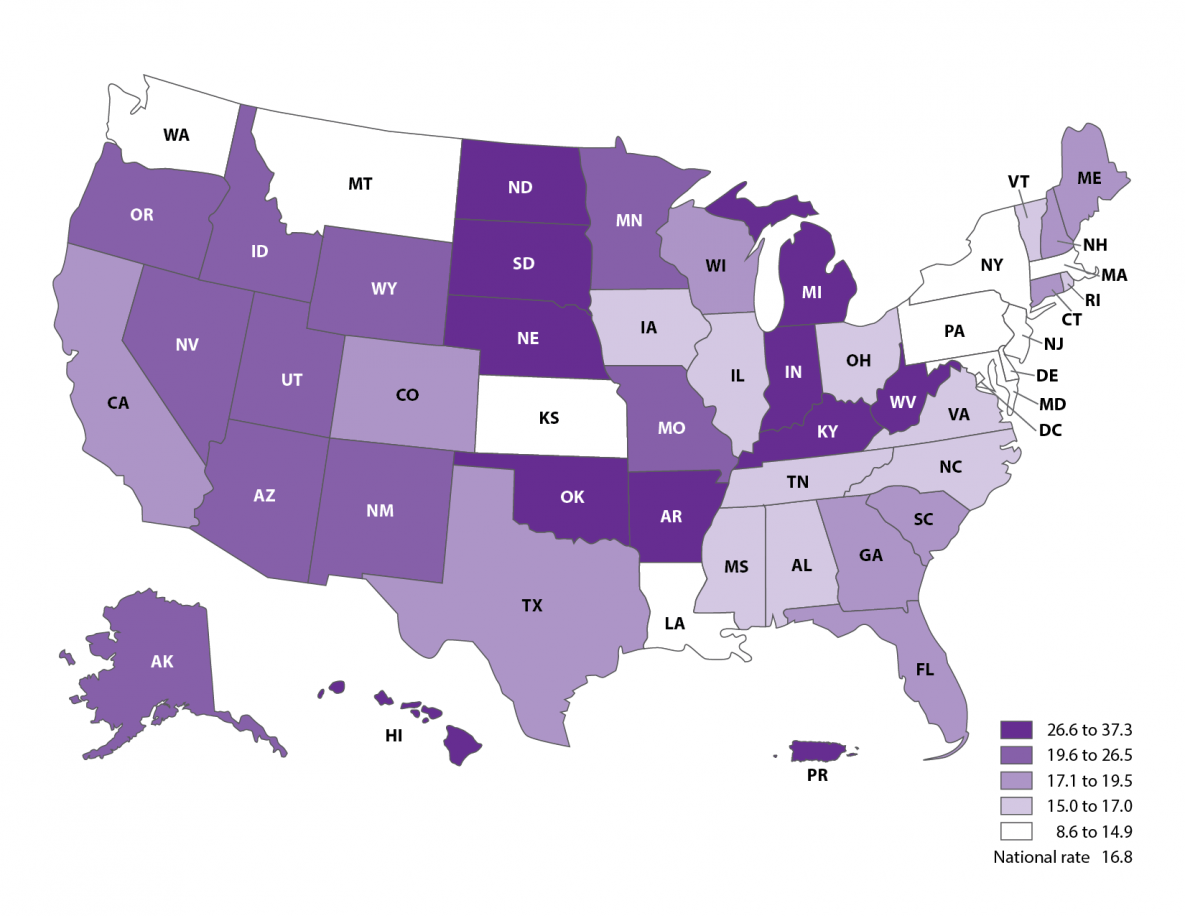
- ART-conceived multiple-birth rates were highest in North Dakota (37.3%), South Dakota (35.5%), and Puerto Rico (35.1%).
- ART-conceived multiple-birth rates were lowest in Delaware (8.6%), Montana (10.2%) and the District of Columbia (10.3%).
Proportion of ART multiples (twins, triplets, etc.) among all multiples, 2019
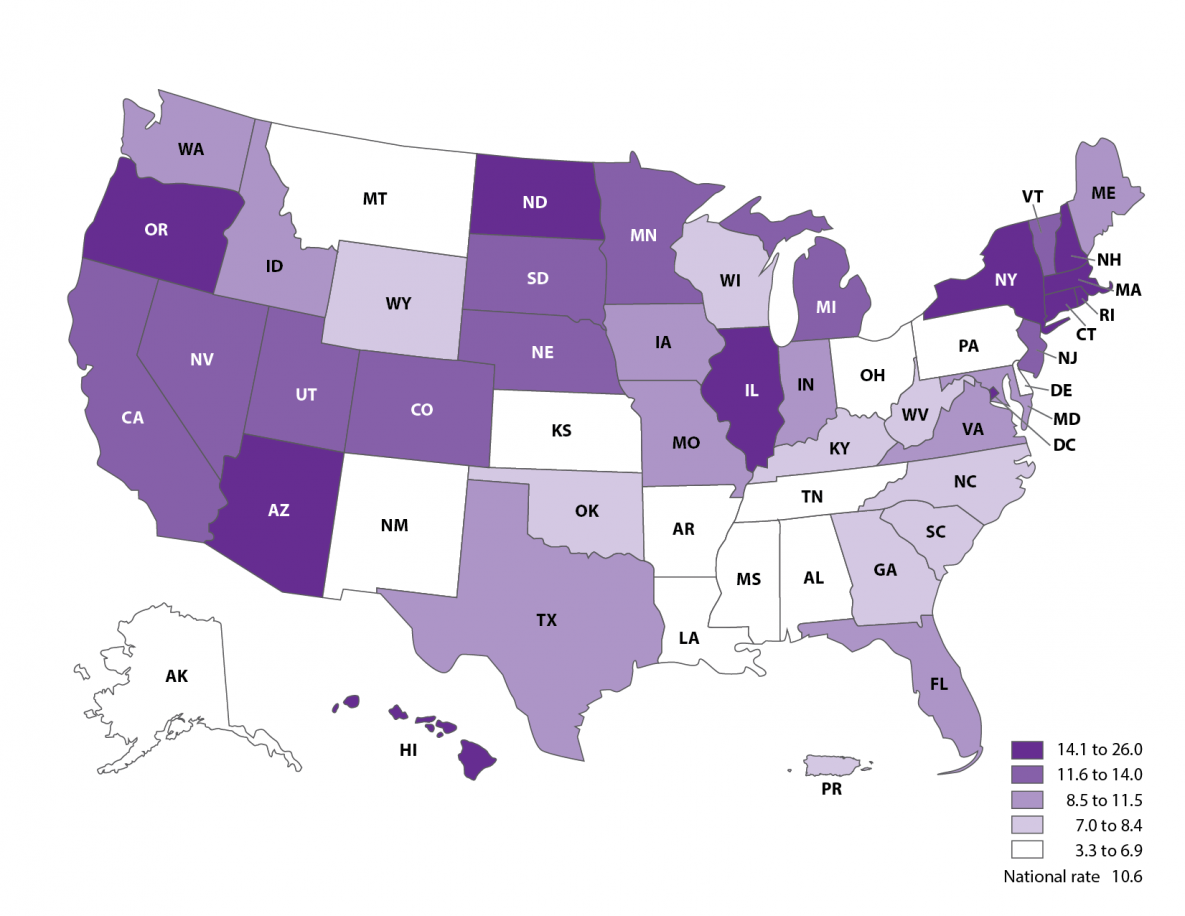
- Nationally, ART-conceived infants accounted for 10.6% of all multiple births.
- The proportion of ART multiples among all multiples was highest in Hawaii (26.0%), Connecticut (21.2%), and Massachusetts (19.4%).
- The proportion of ART multiples among all multiples was lowest in Mississippi (3.3%), Alabama (3.4%), and Montana (4.3%).
Preterm (<37 weeks of gestation) Birth Rates
Preterm birth is when a baby is born before 37 weeks of pregnancy have been completed. Women who conceive through ART are at higher risk for preterm birth, primarily because they are more likely to be pregnant with more than one baby at a time. ART-conceived infants were almost three times more likely to be born preterm (24.4%) than all infants (10.2%) born in the general population. Even among singletons, the rate of preterm births was higher among ART-conceived infants (15.4%) than among all infants (8.5%).
Proportion of ART preterm births among all preterm births, 2019
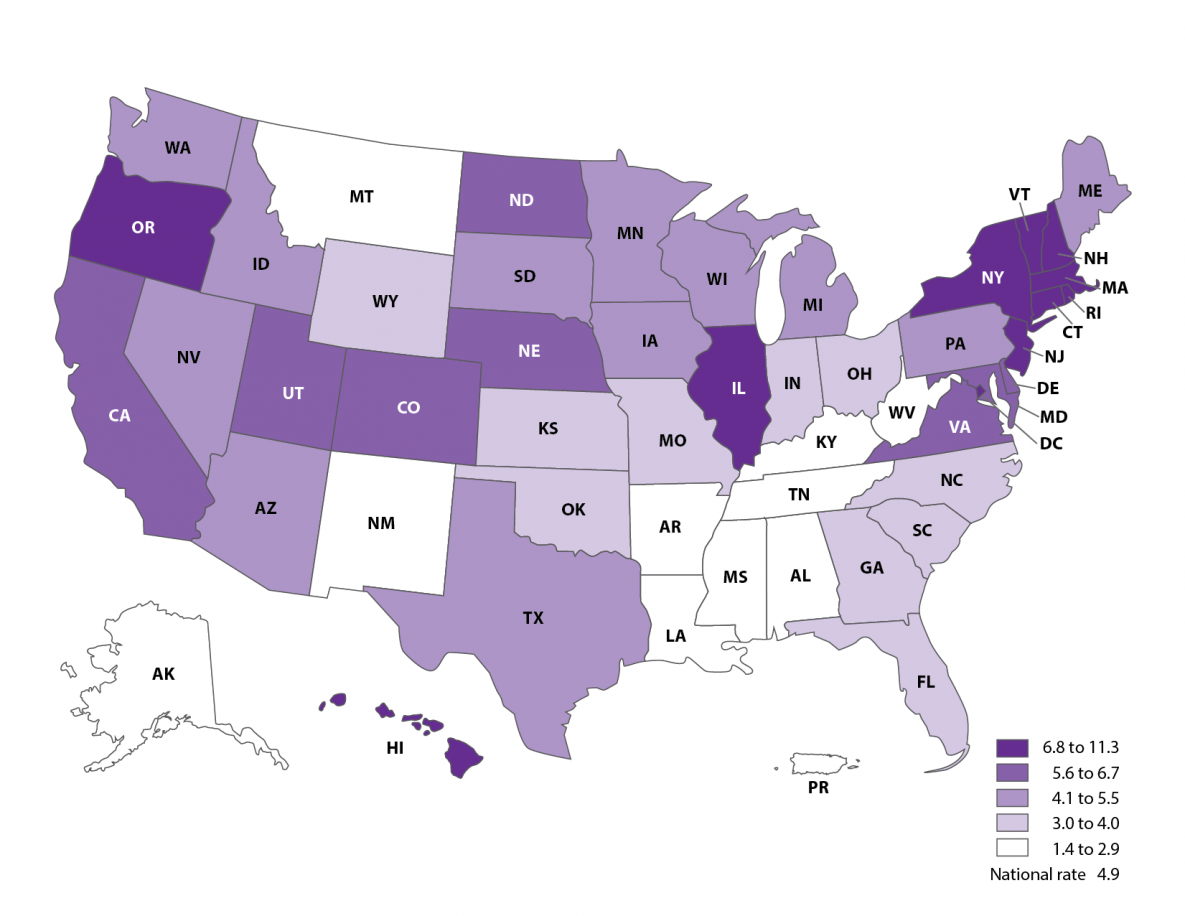
- Nationally, ART-conceived infants accounted for 4.9% of all infants born preterm.
- In two states—Connecticut and Massachusetts—more than 10% of all infants born preterm were conceived with ART.
- The contribution of ART to preterm birth rates was highest in Massachusetts (11.3%) and lowest in Alabama (1.4%).