Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People
COVID-19 Homepage
COVIDView Summary ending on May 2, 2020
Key Updates for Week 18, ending May 2, 2020
Nationally, levels of influenza-like illness (ILI) and COVID-19-like illness (CLI) and the percentage of specimens testing positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to decline. Mortality attributed to COVID-19 also decreased compared to last week but remains elevated above baseline and may increase as additional death certificates are counted.
Virus
Public Health, Commercial and Clinical Laboratories
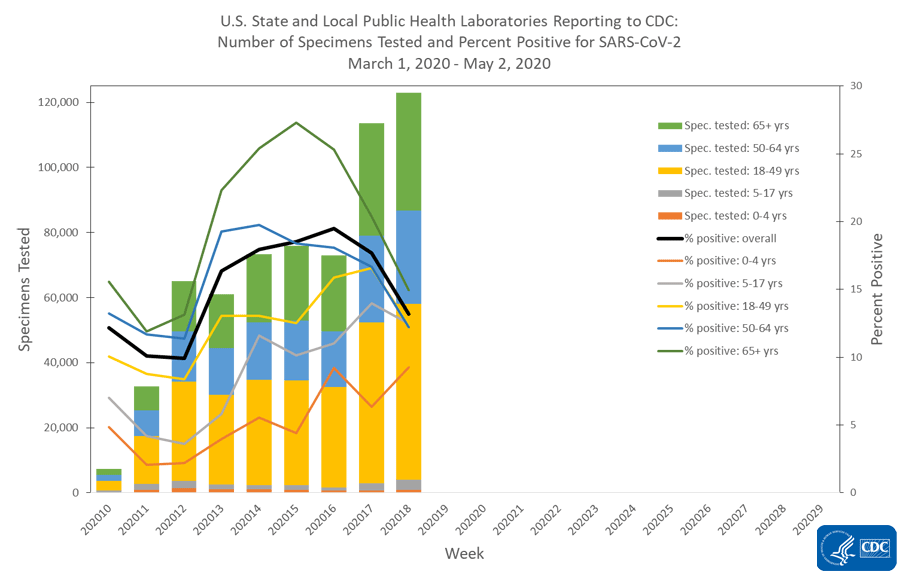
The national percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 at public health, clinical and commercial laboratories decreased from week 17 to week 18. Percentages by type of laboratory:
- Public health laboratories – decreased from 17.7% during week 17 to 13.2% during week 18;
- Clinical laboratories – decreased from 10.3% during week 17 to 9.0% during week 18;
- Commercial laboratories – decreased from 15.9% during week 17 to 13.2% during week 18.
Outpatient and Emergency Department Visits
Outpatient Influenza-Like Illness Network (ILINet) and National Syndromic Surveillance Program (NSSP)
Two indicators from existing surveillance systems are being used to track outpatient or emergency department (ED) visits for illness with symptoms compatible with COVID-19.
- Nationally, the percentages of visits for ILI and COVID-19-like illness (CLI) decreased compared to last week. Levels of ILI are now below baseline nationally for the second week and in all 10 surveillance regions.
Recent changes in health care seeking behavior, including increasing use of telemedicine, recommendations to limit emergency department (ED) visits to severe illnesses, and increased practice of social distancing, are likely affecting data reported from both networks, making it difficult to draw further conclusions at this time. Tracking these systems moving forward will give additional insight into illness related to COVID-19.
Severe Disease
Hospitalizations
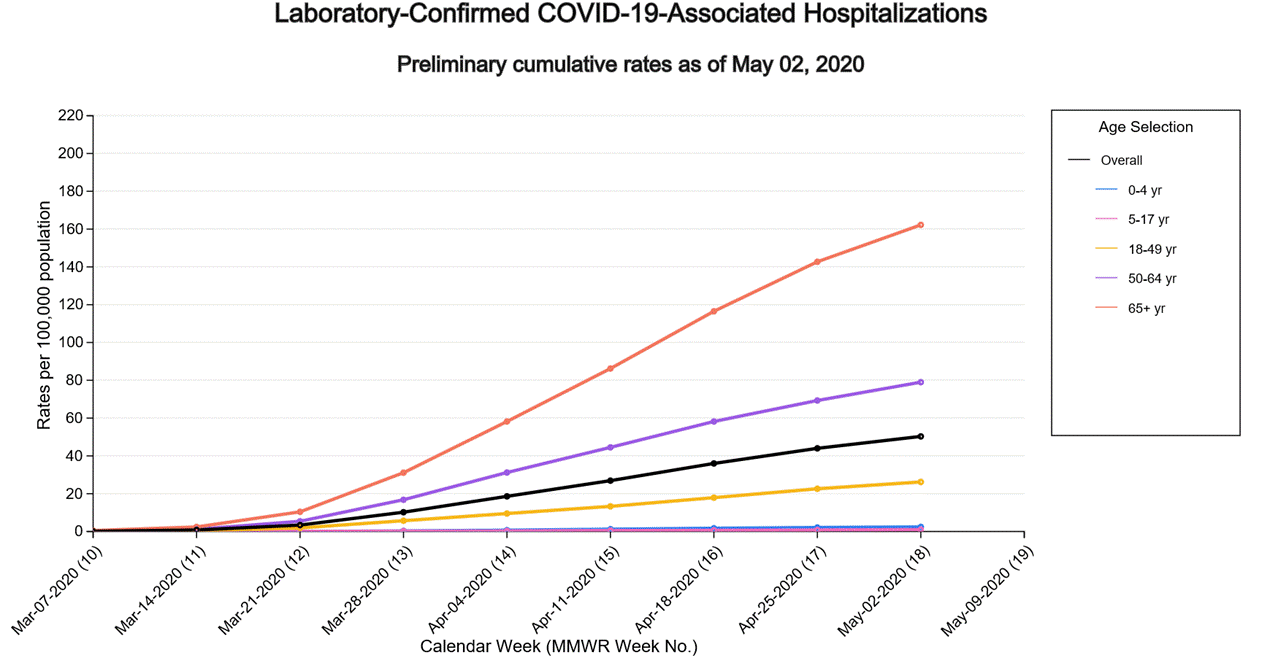
Cumulative COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates since March 1, 2020, are updated weekly. The overall cumulative hospitalization rate is 50.3 per 100,000, with the highest rates in people 65 years and older (162.2 per 100,000) and 50-64 years (79.0 per 100,000).
Mortality
Based on death certificate data, the percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia, influenza or COVID-19 (PIC) decreased from 21.0% during week 17 to 10.6% during week 18 but remained above baseline. This is the third week of a stable or declining percentage of deaths due to PIC, but this percentage may change as death certificates representing recent deaths are processed.
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
A description of the surveillance systems summarized in COVIDView, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component, is available on the surveillance methods page.
Key Points
- Nationally, the percentages of laboratory specimens testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 decreased compared to last week.
- Nationally, visits to outpatient providers and emergency departments (EDs) for illnesses with symptoms consistent with COVID-19 continued to decline and are below baseline nationally and in all regions of the country.
- The decrease in the percentage of people presenting for care with ILI and CLI may be due to a decline in COVID-19 illness, which could be in part a result of widespread adoption of social distancing in addition to changes in healthcare seeking behavior.
- There has been very little influenza virus activityin recent weeks.
- The overall cumulative COVID-19 associated hospitalization rate is 50.3 per 100,000, with the highest rates in people aged 65 years and older (162.2 per 100,000) and 50-64 years (79.0 per 100,000). Hospitalization rates are cumulative and expected to increase as the COVID-19 pandemic continues.
- Hospitalization rates for COVID-19 in adults (18-64 years) are already higher than hospitalization rates for influenza at comparable time points* during the past 5 influenza seasons.
- For people 65 years and older, current COVID-19 hospitalization rates are within ranges observed during comparable time points* in recent influenza seasons.
- For children (0-17 years), COVID-19 hospitalization rates are much lower than influenza hospitalization rates during recent influenza seasons.
- Based on death certificate data, the percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia, influenza or COVID-19 (PIC) decreased from 21.0% during week 17 to 10.6% during week 18 but remained above baseline. This is the third week during which a declining percentage of deaths due to PIC has been seen, but the percentage remains high compared with any influenza season. The percentage may change as additional death certificates for deaths during recent weeks are processed.
*Number of weeks since 10% of specimens tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and influenza, respectively.
The number of specimens tested for SARS-CoV-2 and reported to CDC by public health laboratories and a subset of clinical and commercial laboratories in the United States are summarized below. At this point in the outbreak, all laboratories are performing primary diagnostic functions; therefore, the percentage of specimens testing positive across laboratory types can be used to monitor trends in COVID-19 activity. As the outbreak progresses, it is possible that different types of laboratories will take on different roles, and the data interpretation may need to change. The lower percentage of specimens testing positive in clinical laboratories compared to public health and commercial laboratories may be influenced by COVID-19 activity in areas with reporting laboratories and by larger proportions of specimens obtained from children tested in these laboratories.
| Week 18 (April 26 – May 2, 2020) |
Cumulative since March 1, 2020 | |
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 839,135 | 4,882,263 |
| Public Health Laboratories | 131,001 | 676,488 |
| Clinical Laboratories | 73,113 | 396,585 |
| Commercial Laboratories | 635,021 | 3,809,190 |
| No. of positive specimens (%) | 109,728 (13.1%) | 832,238 (17.0%) |
| Public Health Laboratories | 17,290 (13.2%) | 106,529 (15.7%) |
| Clinical Laboratories | 8,523 (9.0%) | 40,458 (10.2%) |
| Commercial Laboratories | 83,915 (13.2%) | 685,251 (18.0%) |
* Commercial and clinical laboratory data represents select laboratories and does not capture all tests performed in the United States.
Public Health Laboratories
Clinical Laboratories
Commercial Laboratories
* Commercial laboratories began testing for SARS-CoV-2 in early March, but the number and geographic distribution of reporting commercial laboratories became stable enough to calculate a weekly percentage of specimens testing positive as of March 29, 2020.
Additional virologic surveillance information: Surveillance Methods
Outpatient/Emergency Department Illness
Two syndromic surveillance systems are being used to monitor trends in outpatient and emergency department visits that may be associated with COVID-19. Each system monitors a slightly different syndrome, and together these systems provide a more comprehensive picture of mild to moderate COVID-19 illness than either would individually. Both systems are currently being affected by recent changes in healthcare seeking behavior, including increasing use of telemedicine, recommendations to limit emergency department (ED) visits to severe illnesses, and increased practice of social distancing. These changes affect the numbers of people and their reasons for seeking care in the outpatient and ED settings.
ILINet
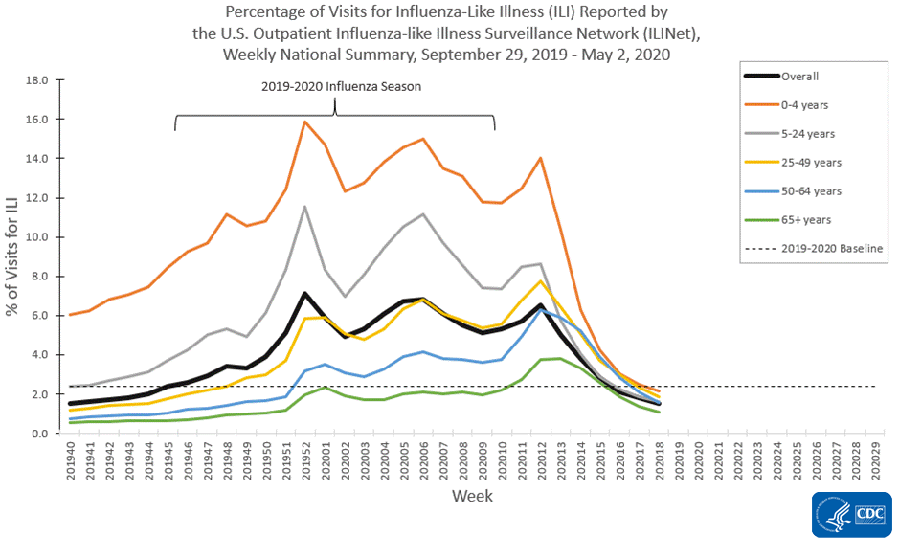
The U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) provides data on visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) (fever [≥100○F] and cough and/or sore throat) to approximately 2,600 primary care providers, emergency departments and urgent care centers in all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Mild COVID-19 illness presents with symptoms similar to ILI, so ILINet is being used to track trends of mild to moderate COVID-19 illness and allows for comparison with prior influenza seasons.
Nationwide during week 18, 1.5% of patient visits reported through ILINet were due to ILI. This percentage is below the national baseline of 2.4% and represents the sixth week of decline after three weeks of increase beginning in early March. The percentage of visits for ILI decreased in all age groups. Nationally, laboratory-confirmed influenza activity as reported by clinical laboratories has decreased to levels usually seen in summer months which, along with changes in healthcare seeking behavior and the impact of social distancing, is likely contributing to the decrease in ILI activity.
* Age-group specific percentages should not be compared to the national baseline.
On a regional levelExternal, the percentage of outpatient visits for ILI ranged from 0.9% to 2.8% during week 18. Compared to week 17, the percent of outpatient visits for ILI increased slightly in region 7, but decreased in all other regions, and all ten regions are below their region-specific baselines.
ILI Activity Levels
Data collected in ILINet are used to produce a measure of ILI activity for all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia and New York City. The mean reported percentage of visits due to ILI for the current week is compared to the mean reported during non-influenza weeks, and the activity levels correspond to the number of standard deviations below, at or above the mean.
The number of jurisdictions at each activity level during week 18 and the change compared to the previous week are summarized in the table below and shown in the following maps. The decreasing percentage of visits for ILI described above are reflected in this week’s ILI activity levels.
| Activity Level | Number of Jurisdictions | |
| Week 18 (Week ending May 2, 2020) |
Compared to Previous Week | |
| Very High | 0 | 0 |
| High | 1 | -2 |
| Moderate | 3 | -4 |
| Low | 3 | No change |
| Minimal | 46 | +6 |
| Insufficient Data* | 1 | No change |
*Data collected in ILINet may disproportionally represent certain populations within a state and may not accurately depict the full picture of influenza activity for the whole state. Differences in the data presented here by CDC and independently by some state health departments likely represent differing levels of data completeness with data presented by the state likely being the more complete.
National Syndromic Surveillance Program (NSSP): Emergency Department (ED) Visits
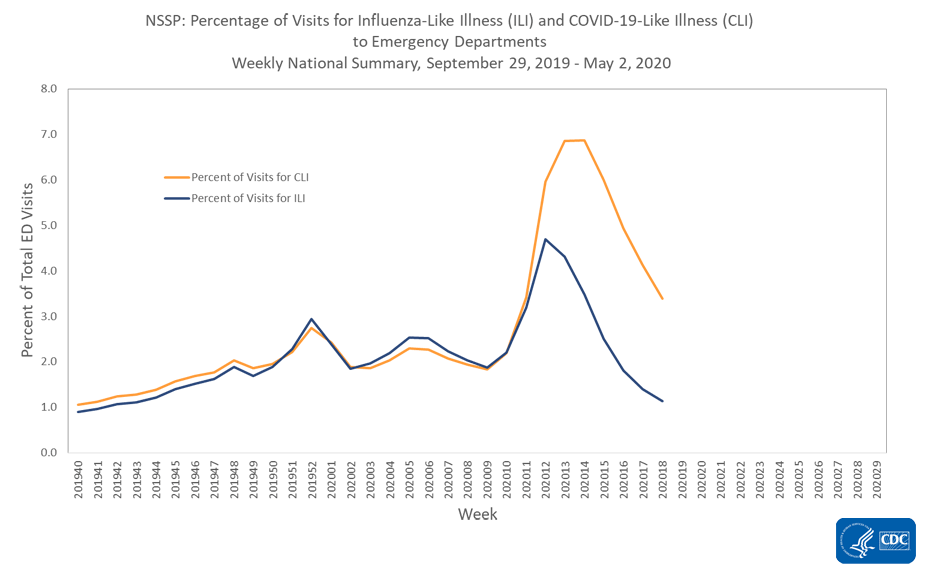
NSSP is a collaboration among CDC, federal partners, local and state health departments and academic and private sector partners to collect, analyze and share electronic patient encounter data received from multiple healthcare settings. To track trends of potential COVID-19 visits, visits for COVID-19-like illness (CLI) (fever and cough or shortness of breath or difficulty breathing or presence of a coronavirus diagnosis code) and ILI to a subset of emergency departments in 47 states are being monitored.
Nationwide during week 18, 3.4% of emergency department visits captured in NSSP were due to CLI and 1.1% were due to ILI. This is the sixth week of decline in percentage of visits for ILI and the fifth week of stable or declining percentage of visits for CLI. All 10 HHS regionsExternal experienced a decline in percentage of visits for ILI and CLI.
Additional information about medically attended outpatient and emergency department visits for ILI and CLI: Surveillance Methods
Hospitalizations
The COVID-19-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) conducts population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed COVID-19-associated hospitalizations in select counties participating in the Emerging Infections Program (EIP) and states participating in the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Project (IHSP). COVID-NET-estimated hospitalization rates are updated weekly.
A total of 16,318 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19-associated hospitalizations were reported by sites between March 1, 2020, and May 2, 2020. The overall cumulative hospitalization rate was 50.3 per 100,000 population. Among the 0-4 years, 5-17 years, 18-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years age groups, the highest rate of hospitalization is among adults aged 65 years (162.2 per 100,000), followed by adults aged 50-64 years (79.0 per 100,000) and adults aged 18-49 years (26.2 per 100,000).
| Age Group | Cumulative Rate per 100,000 Population |
|---|---|
| Overall |
50.3 |
| 0-4 years |
2.4 |
| 5-17 years |
1.0 |
| 18-49 years |
26.2 |
|
18-29 years |
11.8 |
|
30-39 years |
26.1 |
|
40-49 years |
45.0 |
| 50-64 years |
79.0 |
| 65+ years |
162.2 |
|
65-74 years |
118.6 |
|
75-84 years |
194.2 |
|
85+ years |
301.8 |
| Overall | 0-4 years | 5-17 years | 18-49 years | 50-64 years | 65+ years | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Cases with available race | 6,624 (40.6) | 13 (27.7) | 29 (52.7) | 1,451 (38.5) | 1,959 (40.0) | 3,172 (42.0) |
| Non-Hispanic White | 2,682 (40.5) | 5 (38.5) | 5 (17.2) | 321 (22.1) | 647 (33.0) | 1,704 (53.7) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 2,436 (36.8) | 2 (15.4) | 10 (34.5) | 567 (39.1) | 819 (41.8) | 1,038 (32.7) |
| Hispanic | 827 (12.5) | 4 (30.8) | 11 (37.9) | 373 (25.7) | 267 (13.6) | 172 (5.4) |
| Other1 | 679 (10.3) | 2 (15.4) | 3 (10.3) | 190 (13.1) | 226 (11.5) | 258 (8.1) |
| Cases missing race2 | 9,694 (59.4) | 34 (72.3) | 26 (47.3) | 2,319 (61.5) | 2,935 (60.0) | 4,380 (58.0) |
1 Other includes data on persons who are Asian, American Indian/Alaskan Native, Multi-race, and persons for whom race/ethnicity data is unknown; 2 Cases with missing race include those for whom chart reviews have not yet been conducted to ascertain race; these data will be updated as additional race data become available
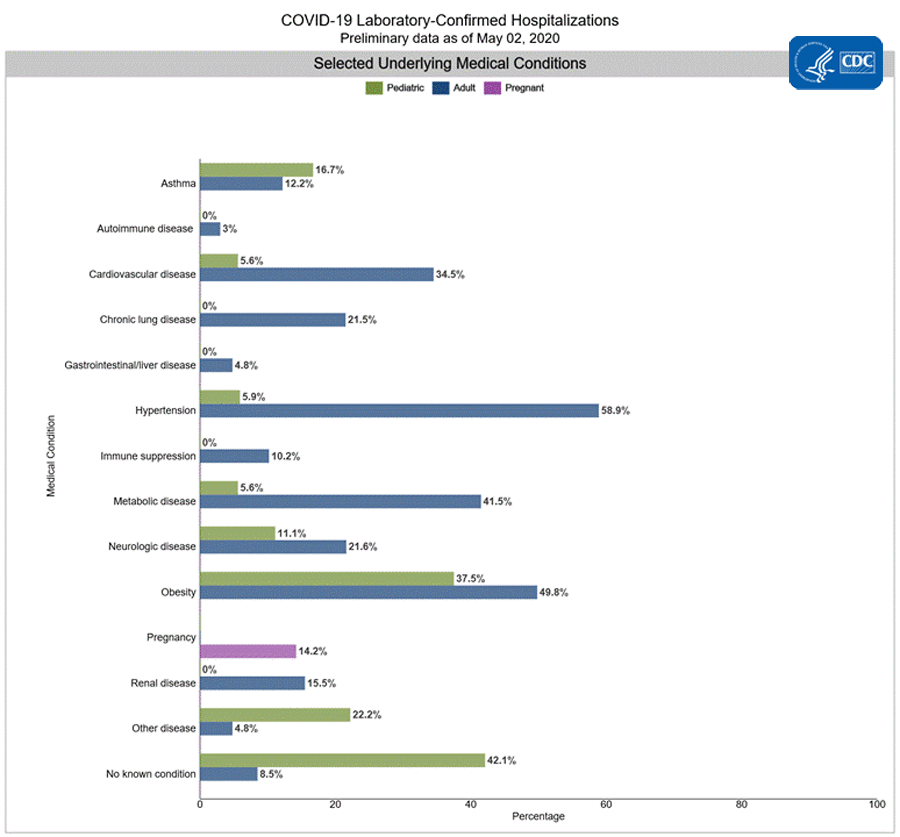
Among 2,876 hospitalized adults with information on underlying medical conditions, 91.5% had at least one reported underlying medical condition, the most commonly reported were hypertension, obesity, chronic metabolic disease, and cardiovascular disease.
Additional hospitalization surveillance information: Surveillance Methods | Additional rate data | Additional demographic and clinical data
Mortality Surveillance
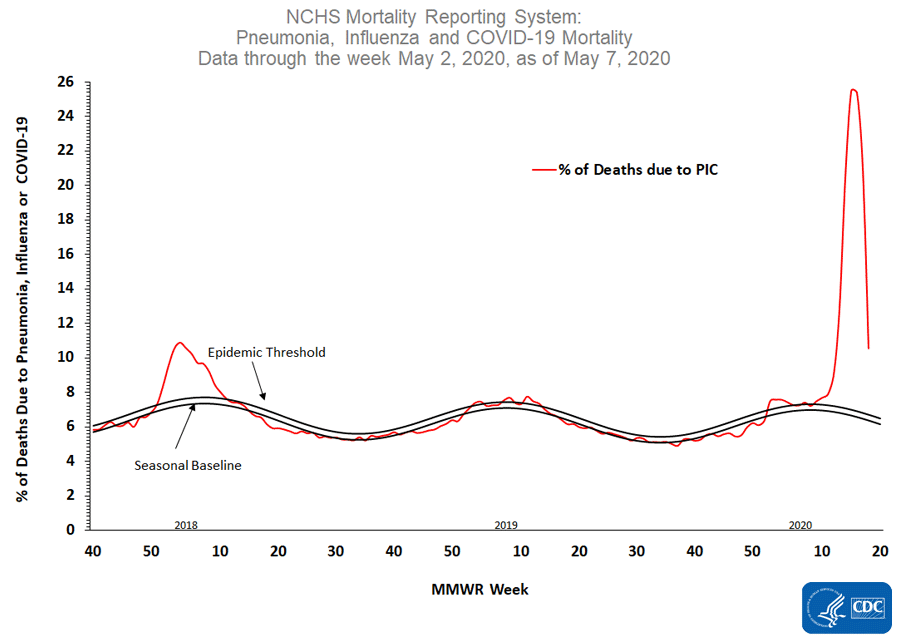
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) collects death certificate data from vital statistics offices for all deaths occurring in the United States. Based on death certificate data available on May 7, 2020, 10.6% of all deaths occurring during the week ending May 2, 2020 (week 18) were due to pneumonia, influenza or COVID-19 (PIC). This is the third week of a stable or declining percentage of deaths due to PIC; however, the percentage remains above the epidemic threshold of 6.7% for week 18. Data for recent weeks are incomplete, and the PIC percentage may increase as more death certificates representing deaths during these weeks are filed.
*Data during recent weeks are incomplete because of the lag in time between when the death occurred and when the death certificate is completed, submitted to NCHS and processed for reporting purposes.
Additional NCHS mortality surveillance information: Surveillance Methods | Provisional Death Counts for COVID-19