Estimated Influenza Illnesses, Medical visits, and Hospitalizations Averted by Vaccination
For the past several years, CDC has estimated the burden of influenza and the impact of annual influenza vaccination in the United States. CDC finds these estimates using a model that estimates the numbers of flu illnesses, medical visits and hospitalization prevented by vaccination using season-specific data on burden of disease, vaccine coverage and vaccine effectiveness (VE). Variations in these three inputs can impact both the burden of disease and the burden averted by vaccination from season to season. CDC uses the estimates of the burden of influenza in the population and the impact of influenza vaccination to inform policy and communications related to influenza.

508 Compliant Text:
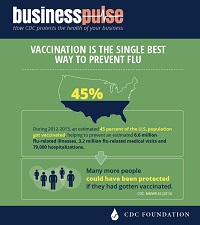
2017-2018 Flu Season: Flu Burden and Flu Burden Averted by Vaccination
During the 2017-2018 flu season, CDC estimates flu caused:
49 million flu illnesses, 960,000 flu hospitalizations, 79,000 flu deaths
This severe season could have been worse without flu vaccines.
Approximately 40% if the U.S. population chose to get a flu vaccine during the 2017-2018 flu season, and this prevented an estimated:
7 million, about the population of New York City.
109,000, or about the number of vehicles crossing the Golden Gate Bridge each day.
8,000, or twice the number of hospitals in the U.S.
Imagine the impact if more Americans chose to get a flu vaccine.
Many more flu illnesses, flu hospitalizations and flu deaths could be prevented.
Get vaccinated