Global Health Security: Prevention
CDC aims to PREVENT avoidable epidemics, including naturally occurring outbreaks and intentional or accidental releases.
This is achieved through the following objectives:
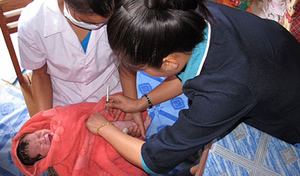
The First dose of hepatitis B vaccine, given within 24 hours of birth, is administered to a baby in Laos.
-
Preventing the emergence and spread of drug-resistant microbes and emerging zoonotic diseases and strengthening international regulatory frameworks governing food safety
- Act to reduce the individual and institutional factors that enable antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of disease threats that move from animals to humans. These are known as zoonotic diseases.
- Increase surveillance and early detection of drug-resistant microorganisms and novel zoonotic diseases.
- Strengthen supply chains.
- Promote safe practices in livestock production and the marketing of animals.
- Promote the appropriate and responsible use of antibiotics in all settings, including developing strategies to improve food safety.
-
Promoting national biosafety and biosecurity systems
- Promote the development of ways for countries to manage biological materials needed for diagnosis, research, and biosurveillance. This effort involves identifying, securing, safely monitoring, and storing dangerous microbes in a minimal number of facilities. It is also necessary to advance safe and responsible conduct for handling microbes.
-
Reducing the number and magnitude of infectious disease outbreaks
- Establish effective programs for vaccination against epidemic-prone diseases and infection control in hospitals.