HTDS Guide – Public Involvement and Scientific Review
‹View Table of Contents
Return to The Hanford Thyroid Disease Study page
Section Summary
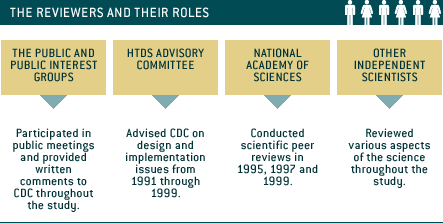
- The public commented on design and implementation issues throughout the study.
- The HTDS Advisory Committee provided ongoing advice to CDC on the design and implementation of the study.
- A committee of the National Academy of Sciences peer reviewed the HTDS at three points: Pilot Study, Analysis Plan and HTDS Draft Report.
- CDC convened other independent scientists to review the HTDS Draft Report.
Throughout the study, HTDS researchers received input and suggestions from a wide variety of sources.
The Public
Individuals and public groups provided input in a variety of ways, including participation in public meetings and the HTDS Advisory Committee, and with written comments to CDC.
The research team communicated with the public throughout the study using newsletters, mailers and a toll-free number. Under a separate project funded by the Federal Government, the Hanford Health Information Network provided information about radiation health effects.
The HTDS Advisory Committee
The HTDS Advisory Committee (officially known as the Hanford Thyroid Morbidity Study Advisory Committee) was created to advise CDC on the design and implementation of the study.
The committee was chartered by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Scientists, state health officials, environmental groups, Indian Nations and the public were represented in the group.
The committee met regularly from 1991 through 1999. At each meeting the public was given an opportunity to ask questions and offer their own views on the study.
National Academy of Sciences (NAS)
The NAS is one of the country’s most respected scientific organizations. At three points in the study (Pilot Study, Analysis Plan and HTDS Draft Report), an NAS committee peer reviewed the study and made recommendations to the research team. The NAS committee included epidemiologists, statisticians and other scientists.
Peer review is an independent scientific evaluation that helps ensure that a study is of high quality.
Independent Scientists
In 1998, CDC convened a group of independent scientists with expertise in thyroid disease, radiation and epidemiology to review the HTDS Draft Report. Their evaluation was made available in a public report.
Other independent scientists offered critical review on the pilot study design and protocol during the early phase of the study.
The HTDS involved extensive scientific peer review and public involvement.
Study Design
The study design, or protocol, describes all the methods used for conducting the study, such as recruiting participants and conducting thyroid examinations.
Public interest groups, scientists and members of the public were invited to comment on the protocol in public meetings in the Northwest. They were also encouraged to send written comments to CDC.
The protocol was evaluated by the HTDS Advisory Committee, and approved by CDC, the Institutional Review Board of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the Federal Office of Management and Budget.
Pilot Study
In the early 1990s, researchers began recruiting participants and collecting data for a pilot study to determine the feasibility of a large-scale epidemiologic study. A Pilot Study Report was issued in 1994, peer reviewed by the NAS, and approved by the HTDS Advisory Committee. In 1995, both panels agreed that a full-scale epidemiologic study was feasible. The NAS also recommended that the researchers develop an analysis plan describing how the data would be analyzed.
Analysis Plan
The Analysis Plan was completed in 1997 and peer reviewed by the NAS. It was also reviewed and approved by the HTDS Advisory Committee. In addition, the public was invited to offer its own views on the plan.
HTDS Draft Report
CDC released the HTDS Draft Report in January 1999. An extensive review by the NAS concluded that the study was scientifically sound but had probably overstated the certainty of the findings. The NAS recommended a number of technical revisions and clarifications.
Following the review, the research team conducted additional technical work to address the NAS recommendations as well as those received from the public and other independent scientists. The HTDS Final Report represents completion of the study.