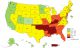
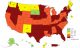
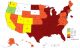
Adult Physical Inactivity Prevalence Maps by Race/Ethnicity 2015-2018
(January 2020)—According to new state maps of adult physical inactivity, all states and territories had more than 15% of adults who were physically inactive, and this estimate ranged from 17.3 to 47.7%. Inactivity levels vary among adults by race/ethnicity and location.
Physical inactivity is defined as self-report of engaging in no leisure-time physical activity during the past month. The data come from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), an ongoing state-based, telephone interview survey conducted by CDC and state health departments.
The maps use combined data from 2015 through 2018 and show noticeable differences in the prevalence of physical inactivity by race/ethnicity. Hispanic adults (31.7%) had the highest prevalence of physical inactivity, followed by non-Hispanic Black (30.3%) and non-Hispanic White adults (23.4%). In the majority of states, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults had a significantly higher prevalence of inactivity than non-Hispanic White adults.
- 5 states and Puerto Rico had a physical inactivity prevalence of 30% or higher among non-Hispanic White adults.
- 22 states and Puerto Rico had a physical inactivity prevalence of 30% or higher among Hispanic adults.
- 23 states and the District of Columbia had a physical inactivity prevalence of 30% or higher among non-Hispanic Black adults.
Across States and Territories
- All states and territories had more than 15% of adults who were physically inactive.
- In 4 states (Colorado, Washington, Utah, and Oregon) and the District of Columbia, 15% to less than 20% of adults were physically inactive.
- In 24 states, 20% to less than 25% of adults were physically inactive.
- In 15 states, 25% to less than 30% of adults were physically inactive.
- In 7 states (Tennessee, Oklahoma, Louisiana, Alabama, Kentucky, Arkansas, and Mississippi), and 2 US territories (Puerto Rico, and Guam), 30% or more of adults were physically inactive.
- The South (28.0%) had the highest prevalence of physical inactivity, followed by the Northeast (25.6%), Midwest (25.0%), and the West (20.5%).
Map: Overall Physical Inactivity
Prevalence of Self-Reported Physical Inactivity* Among US Adults by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2015–2018
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System
* Respondents were classified as physically inactive if they responded “no” to the following question: “During the past month, other than your regular job, did you participate in any physical activities or exercises such as running, calisthenics, golf, gardening, or walking for exercise?”
** Sample size <50 or the relative standard error (dividing the standard error by the prevalence) ≥30%.
| Prevalence of Self-Reported Physical Inactivity by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2015-2018 | ||
|---|---|---|
| State | Prevalence | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Alabama | 31.0 | (30.2, 31.7) |
| Alaska | 20.3 | (19.1, 21.5) |
| Arizona | 23.7 | (23.0, 24.4) |
| Arkansas | 32.5 | (31.4, 33.6) |
| California | 20.4 | (19.9, 20.9) |
| Colorado | 17.3 | (16.8, 17.8) |
| Connecticut | 22.7 | (22.1, 23.3) |
| Delaware | 28.4 | (27.4, 29.3) |
| District of Columbia | 19.8 | (18.9, 20.8) |
| Florida | 28.0 | (27.4, 28.7) |
| Georgia | 28.5 | (27.7, 29.2) |
| Hawaii | 21.6 | (20.9, 22.3) |
| Idaho | 21.5 | (20.6, 22.3) |
| Illinois | 24.3 | (23.6, 25.1) |
| Indiana | 28.3 | (27.6, 28.9) |
| Iowa | 24.2 | (23.5, 24.8) |
| Kansas | 25.0 | (24.5, 25.4) |
| Kentucky | 32.2 | (31.4, 33.0) |
| Louisiana | 30.9 | (29.9, 31.8) |
| Maine | 23.2 | (22.6, 23.9) |
| Maryland | 23.9 | (23.3, 24.5) |
| Massachusetts | 23.3 | (22.6, 24.0) |
| Michigan | 25.1 | (24.5, 25.6) |
| Minnesota | 21.2 | (20.8, 21.6) |
| Mississippi | 33.0 | (32.1, 33.9) |
| Missouri | 26.8 | (26.0, 27.5) |
| Montana | 22.5 | (21.8, 23.3) |
| Nebraska | 24.2 | (23.7, 24.7) |
| Nevada | 25.6 | (24.5, 26.7) |
| New Hampshire | 21.8 | (21.0, 22.5) |
| New Jersey | 28.7 | (27.7, 29.6) |
| New Mexico | 22.3 | (21.6, 23.1) |
| New York | 26.6 | (26.0, 27.1) |
| North Carolina | 24.7 | (24.0, 25.4) |
| North Dakota | 24.6 | (23.9, 25.4) |
| Ohio | 27.0 | (26.3, 27.6) |
| Oklahoma | 30.2 | (29.4, 31.0) |
| Oregon | 19.2 | (18.5, 19.8) |
| Pennsylvania | 24.8 | (24.1, 25.6) |
| Rhode Island | 25.9 | (25.1, 26.8) |
| South Carolina | 27.2 | (26.6, 27.8) |
| South Dakota | 22.3 | (21.4, 23.2) |
| Tennessee | 30.0 | (29.2, 30.9) |
| Texas | 27.9 | (27.1, 28.7) |
| Utah | 18.6 | (18.1, 19.0) |
| Vermont | 20.5 | (19.8, 21.2) |
| Virginia | 24.0 | (23.4, 24.7) |
| Washington | 18.3 | (17.9, 18.8) |
| West Virginia | 29.8 | (29.0, 30.5) |
| Wisconsin | 21.4 | (20.6, 22.2) |
| Wyoming | 24.1 | (23.3, 25.0) |
| Guam | 31.0 | (29.3, 32.7) |
| Puerto Rico | 47.7 | (46.8, 48.6) |
Maps: Physical Inactivity by Race/Ethnicity
Prevalence of Self-Reported Physical Inactivity Among US Adults by Race/Ethnicity, State and Territory, BRFSS, 2015–2018
Prevalence of Self-Reported Physical Inactivity* Among Non-Hispanic Black Adults by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2015–2018
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System
* Respondents were classified as physically inactive if they responded “no” to the following question: “During the past month, other than your regular job, did you participate in any physical activities or exercises such as running, calisthenics, golf, gardening, or walking for exercise?”
** Sample size <50 or the relative standard error (dividing the standard error by the prevalence) ≥30%.
| Prevalence of Self-Reported Physical Inactivity Among Non-Hispanic Black Adults by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2015-2018 | ||
|---|---|---|
| State | Prevalence | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Alabama | 34.3 | (32.7, 35.9) |
| Alaska | 26.5 | (17.3, 38.3) |
| Arizona | 27.1 | (23.0, 31.6) |
| Arkansas | 34.4 | (31.2, 37.7) |
| California | 23.0 | (20.6, 25.5) |
| Colorado | 20.5 | (17.6, 23.8) |
| Connecticut | 28.6 | (26.4, 30.9) |
| Delaware | 31.9 | (29.4, 34.6) |
| District of Columbia | 30.8 | (29.3, 32.3) |
| Florida | 31.7 | (29.6, 33.8) |
| Georgia | 31.0 | (29.4, 32.6) |
| Hawaii | 26.9 | (19.8, 35.4) |
| Idaho | Insufficient data** | Insufficient data** |
| Illinois | 30.1 | (27.8, 32.5) |
| Indiana | 31.7 | (29.1, 34.4) |
| Iowa | 28.4 | (23.8, 33.4) |
| Kansas | 29.4 | (27.0, 31.9) |
| Kentucky | 32.1 | (28.8, 35.6) |
| Louisiana | 35.1 | (33.1, 37.2) |
| Maine | 29.6 | (18.8, 43.2) |
| Maryland | 26.4 | (25.2, 27.7) |
| Massachusetts | 27.4 | (24.2, 30.8) |
| Michigan | 31.1 | (29.4, 32.9) |
| Minnesota | 26.7 | (24.4, 29.1) |
| Mississippi | 35.2 | (33.6, 36.8) |
| Missouri | 35.1 | (32.3, 38.0) |
| Montana | Insufficient data** | Insufficient data** |
| Nebraska | 25.4 | (22.0, 29.1) |
| Nevada | 29.9 | (25.7, 34.4) |
| New Hampshire | 32.4 | (22.0, 45.0) |
| New Jersey | 32.8 | (30.1, 35.5) |
| New Mexico | 23.8 | (17.8, 31.1) |
| New York | 30.2 | (28.6, 31.8) |
| North Carolina | 28.2 | (26.5, 30.0) |
| North Dakota | 34.3 | (27.2, 42.3) |
| Ohio | 32.6 | (30.3, 34.9) |
| Oklahoma | 33.5 | (30.3, 36.9) |
| Oregon | 17.9 | (12.6, 24.8) |
| Pennsylvania | 27.7 | (25.4, 30.3) |
| Rhode Island | 28.5 | (24.5, 32.9) |
| South Carolina | 31.4 | (30.1, 32.7) |
| South Dakota | Insufficient data** | Insufficient data** |
| Tennessee | 32.1 | (29.5, 34.8) |
| Texas | 30.2 | (27.5, 33.0) |
| Utah | 23.4 | (17.1, 31.1) |
| Vermont | 30.0 | (19.7, 42.8) |
| Virginia | 29.7 | (28.1, 31.3) |
| Washington | 21.6 | (18.7, 24.9) |
| West Virginia | 29.9 | (25.6, 34.6) |
| Wisconsin | 35.3 | (30.3, 40.7) |
| Wyoming | 26.0 | (15.9, 39.5) |
| Guam | Insufficient data** | Insufficient data** |
| Puerto Rico | Insufficient data** | Insufficient data** |
| **Sample size <50 or the relative standard error (dividing the standard error by the prevalence) ≥30%. | ||