Making Health Care Safer infographic
Vital Signs
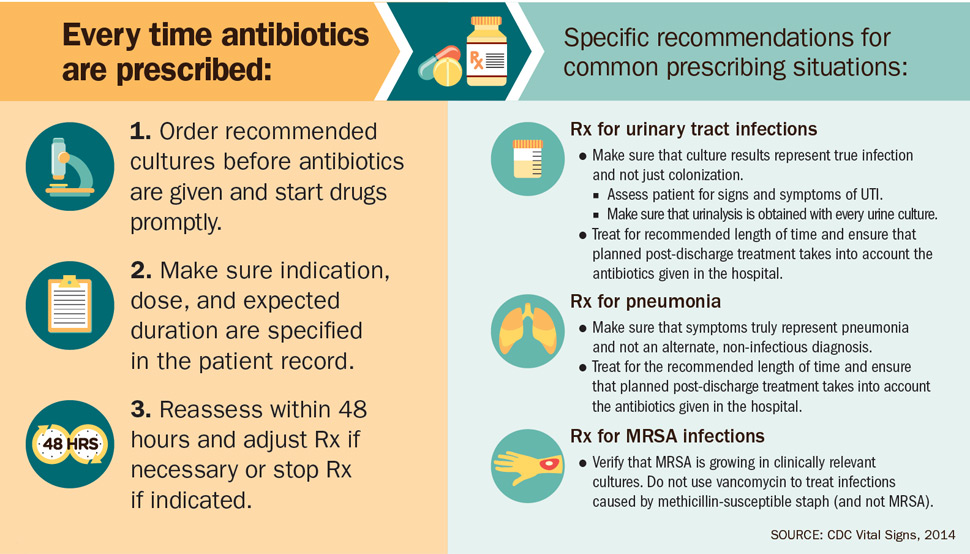
Every time antibiotics are prescribed:
- Icon: Microscope
Text: Order recommended cultures before antibiotics are given and start drugs promptly. Order recommended cultures before antibiotics are given and start drugs promptly. - Icon: Clipboard
Text: Make sure indication, dose, and expected duration are specified in the patient record. - Icon: Clock representing 48 hours.
Text: Reassess within 48 hours and adjust Rx if necessary or stop Rx if indicated.
Specific recommendations for common prescribing situations:
Icon: Pill bottle representing a prescription for urinary tract infections
Text: Rx for urinary tract infections
- Make sure that culture results represent true infection and not just colonization.
- Assess patient for signs and symptoms of UTI.
- Make sure that urinalysis is obtained with every urine culture.
- Treat for recommended length of time and ensure that planned post-discharge treatment takes into account the antibiotics given in the hospital.
Icon: Lungs
Text: Rx for pneumonia
- Make sure that symptoms truly represent pneumonia and not an alternate, non-infectious diagnosis.
- Treat for the recommended length of time and ensure that planned post-discharge treatment takes into account the antibiotics given in the hospital.
Icon: An arm with a methicillin-susceptible staph infection
Text: Rx for MRSA infections
- Verify that MRSA is growing in clinically relevant cultures. Do not use vancomycin to treat infections caused by methicillin-susceptible staph (and not MRSA).
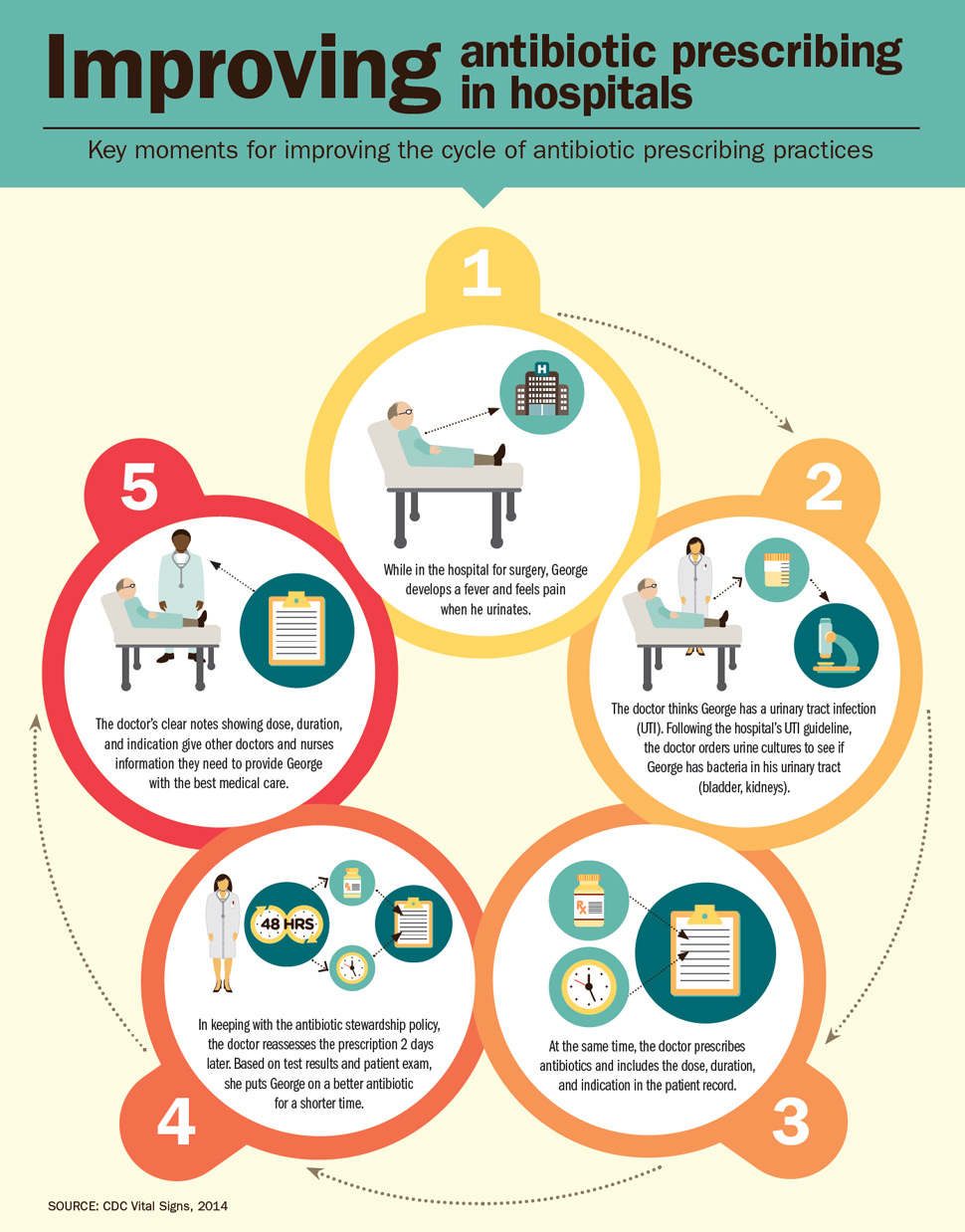
Improving antibiotic prescribing in hospitals: Key moments for improving the cycle of antibiotic prescribing practices.
Graphic 1: George is lying in blue hospital gown on a white hospital bed.
Text: While in the hospital for surgery, George develops a fever and feels pain when he urinates.
Graphic 2: George is talking to a hospital doctor about urine cultures for the hospital to look at under a microscope.
Text: The doctor thinks George has a urinary tract infection (UTI). Following the hospital’s UTI guideline, the doctor orders urine cultures to see if George has bacteria in his urinary tract (bladder, kidneys).
Graphic 3: A prescription bottle and a clock representing the time are noted on a clipboard.
Text: At the same time, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and includes the dose, duration, and indication in the patient record.
Graphic 4: The hospital doctor working with George reviews the clipboard.
Text: In keeping with the antibiotic stewardship policy, the doctor reassesses the prescription the next day. Based on test results and patient exam, she puts George on a better antibiotic for a shorter time.
Graphic 5: George is in his hospital bed talking to a different hospital doctor. The new doctor is reviewing the clipboard with the notes from the previous doctor.
Text: The doctor’s clear notes showing dose, duration, and indication gives other doctors and nurses information they needed to provide George with the best medical care.
