Infographic Binge Drinking: A Dangerous Problem among Women and Girls infographic
Infographic Binge Drinking: A Dangerous Problem among Women and Girls infographic
Vital Signs
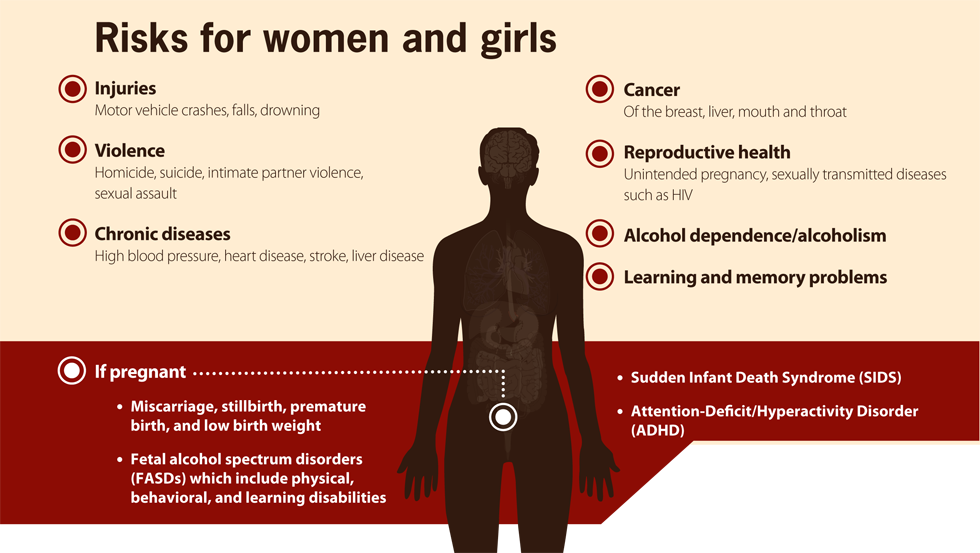
Risks for women and girls
- Injuries
- motor vehicle crashes
- falls
- drowning
- Violence
- homicide
- suicide
- intimate partner violence
- sexual assault
- Chronic diseases
- high blood pressure
- heart disease
- stroke
- liver disease
- cancer of the breast, liver, mouth, and throat
- Reproductive health
- unintended pregnancy
- sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV
- Alcohol dependence/alcoholism
- Learning and memory problems
- If pregnant
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, and low birth weight
- Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) which include physical, behavioral, and learning disabilities
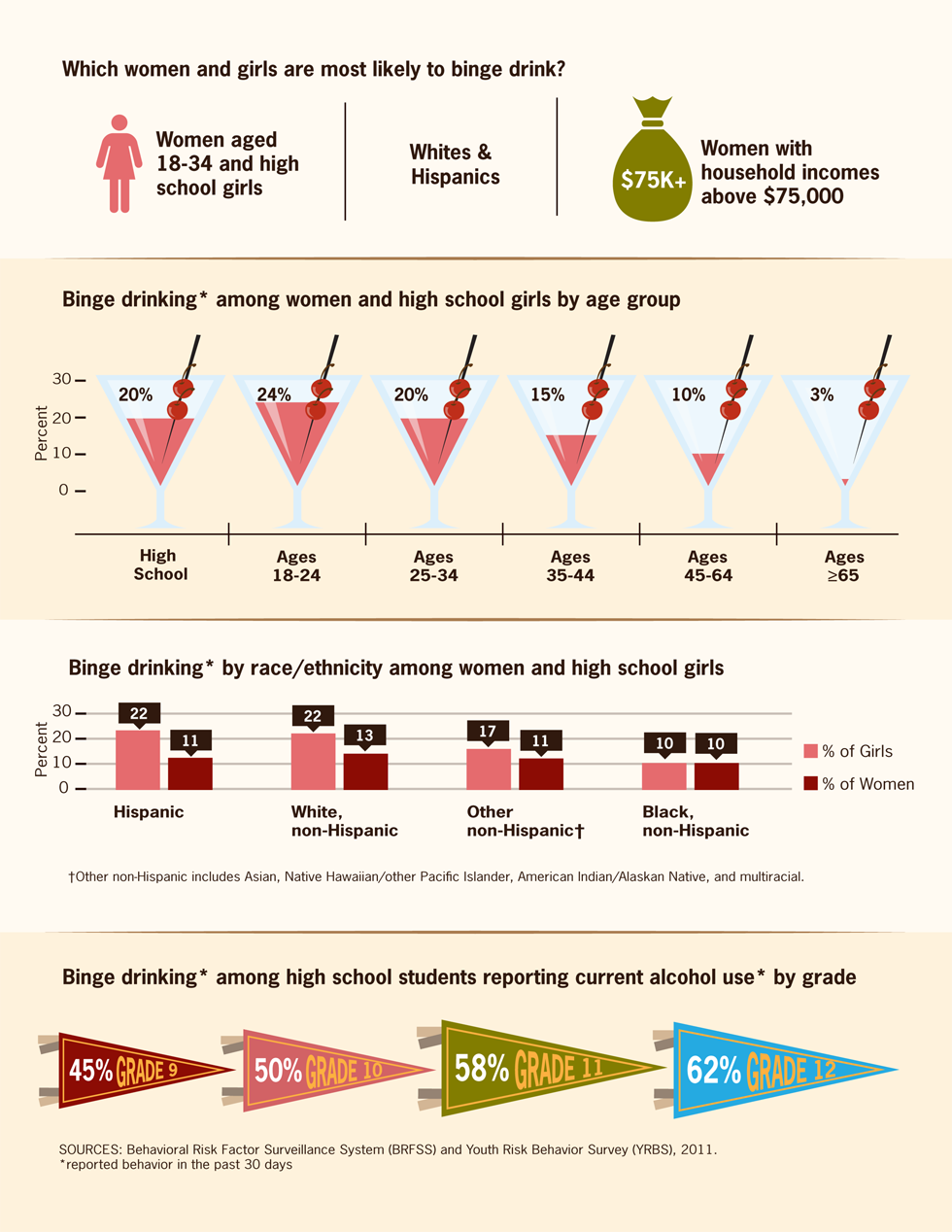
Which women and girls are most likely to binge drink?
- Women aged 18-34 and high school girls
- Whites & Hispanics
- Women with household incomes above $75,000
Binge drinking* among women and high school girls by age group
- High School – 20%
- Ages 18-24 – 24%
- Ages 25-34 – 20%
- Ages 35-44: 15%
- Ages 45-64: 10%
- Ages ≥65: 3%
Binge drinking* by race/ethnicity among women and high school girls
- Hispanic: 22% Girls, 11% Women
- White, non-Hispanic: 22% Girls, 13% Women
- Other, non-Hispanic†: 17% Girls, 11% Women
- Black, non-Hispanic: 10% Girls, 10% Women
†Other non-Hispanic includes Asian, Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander, American Indian/Alaskan Native, and multiracial.
Binge drinking* among high school students reporting current alcohol use* by grade
- Grade 9: 45%
- Grade 10: 50%
- Grade 11: 58%
- Grade 12: 62%
*reported behavior in the past 30 days
SOURCES: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS), 2011.
