Child Injury
April 2012



1 Child
Every hour, one child dies from an injury.

1 in 5
About 1 in 5 child deaths is due to injury.

4 Seconds
Every 4 seconds, a child is treated for an injury in an emergency department.
Child injuries* are preventable, yet more than 9,000 children died from injuries in the US in 2009. Car crashes, suffocation, drowning, poisoning, fires, and falls are some of the most common ways children are hurt or killed. The number of children dying from injury dropped nearly 30% over the last decade. However, injury is still the number 1 cause of death among children. More can be done to keep our children safe.
* ‘Child injuries’ refers to unintentional injuries that occur among children and teens 0-19 years.
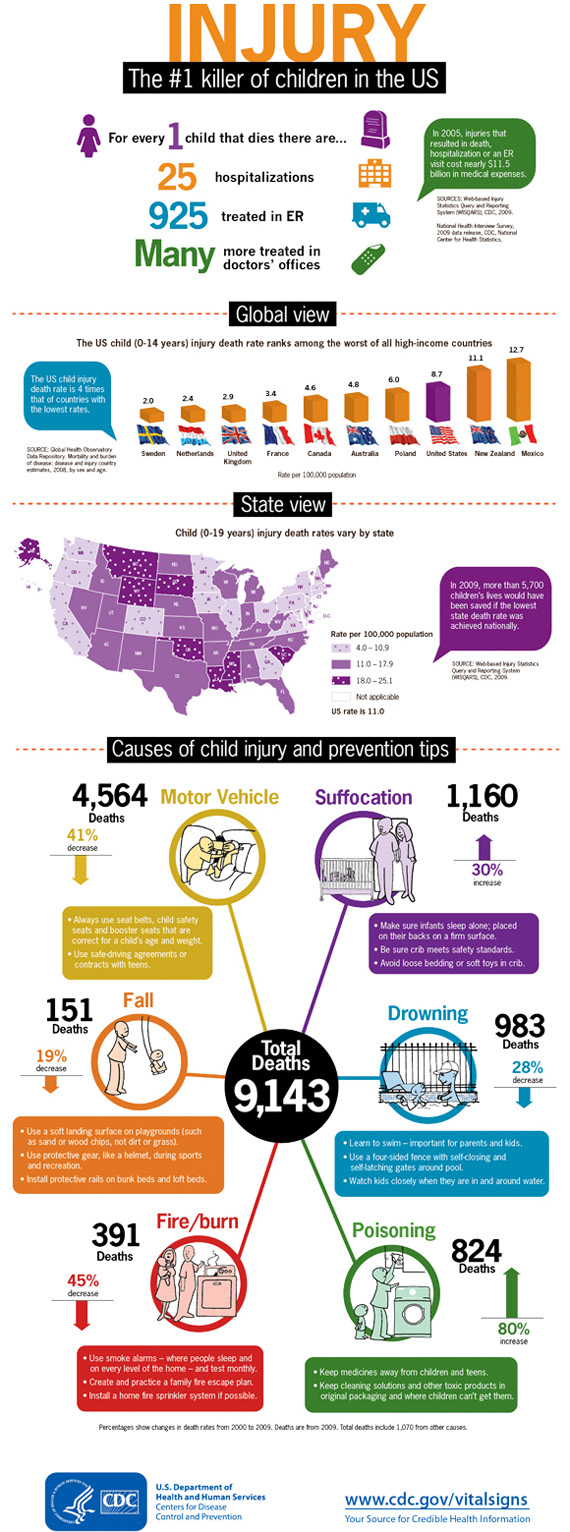
Injuries are the #1 cause of death among children. Car crashes, suffocation, drowning, poisoning, fires, and falls are some of the most common causes of injury. Learn how you can help save lives and prevent these injuries.
States and communities can
- Align efforts with the National Action Plan for Child Injury Prevention, released in 2012 by CDC and more than 60 partner organizations.
- Strengthen data collection on child injury to identify problems and track progress.
- Use strategies shown to reduce injuries such as graduated driver licenses, learn-to-swim programs, and prescription drug monitoring programs.
- Improve access to poison control centers, trauma center care, and preventive services (such as CPR/first aid training).
Health care systems can
- Use technology, such as electronic medical records, to improve the speed and quality of care for injured children, and to monitor the number and severity of injuries.
- Include child safety education for new parents and at all pediatric visits.
Employers can
- Protect all employees, including youth, from workplace injuries by complying with existing safety standards and regulations.
- Provide proper safety training, education, and protective equipment for each job task.
Everyone can
- Take steps to prevent child injury where you live, work, and play.
- Be a good role model—wear a seat belt, use a helmet, and follow other safety tips.
- Learn more about protecting the ones you love at “Injuries Among Children and Teens”.
- Vital Signs: Unintentional Injury Deaths Among Persons Aged 0-19 Years – United States, 2000-2009: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
- Color Me Safe
- Child Injury: What You Need to Know [Podcast – 1:15 minutes]
- Lesiones infantiles: Lo que necesita saber [Podcast – 1:29 minutes]
- Child Injury: What You Need to Know [PSA – 60 seconds]
On Other Web Sites
- Consumer Product Safety Commission
- Consumer Product Safety Commission Pool Safely
- Federal Emergency Management Administration: Fires
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
- MedlinePlus-Child Safety
- MedlinePlus-Drugs and Young People
- MedlinePlus-Infant and Newborn Care
- MedlinePlus-Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
