Vital Signs: Daily Pill Can Prevent HIV
Reaching people who could benefit from PrEP

Preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a medicine taken daily that can be used to prevent getting HIV. PrEP is for people without HIV who are at very high risk for getting it from sex or injection drug use. People at high risk who should be offered PrEP include about 1 in 4 sexually active gay and bisexual men*, 1 in 5 people who inject drugs, and 1 in 200 sexually active heterosexual adults. When taken every day, PrEP is safe and highly effective in preventing HIV infection. PrEP is even more effective if it is combined with other ways to prevent new HIV infections like condom use, drug abuse treatment, and treatment for people living with HIV to reduce the chance of passing the virus to others. Many people who can benefit from PrEP aren’t taking it. If more health care providers know about and prescribe PrEP, more HIV infections could be prevented.
Health care providers can:
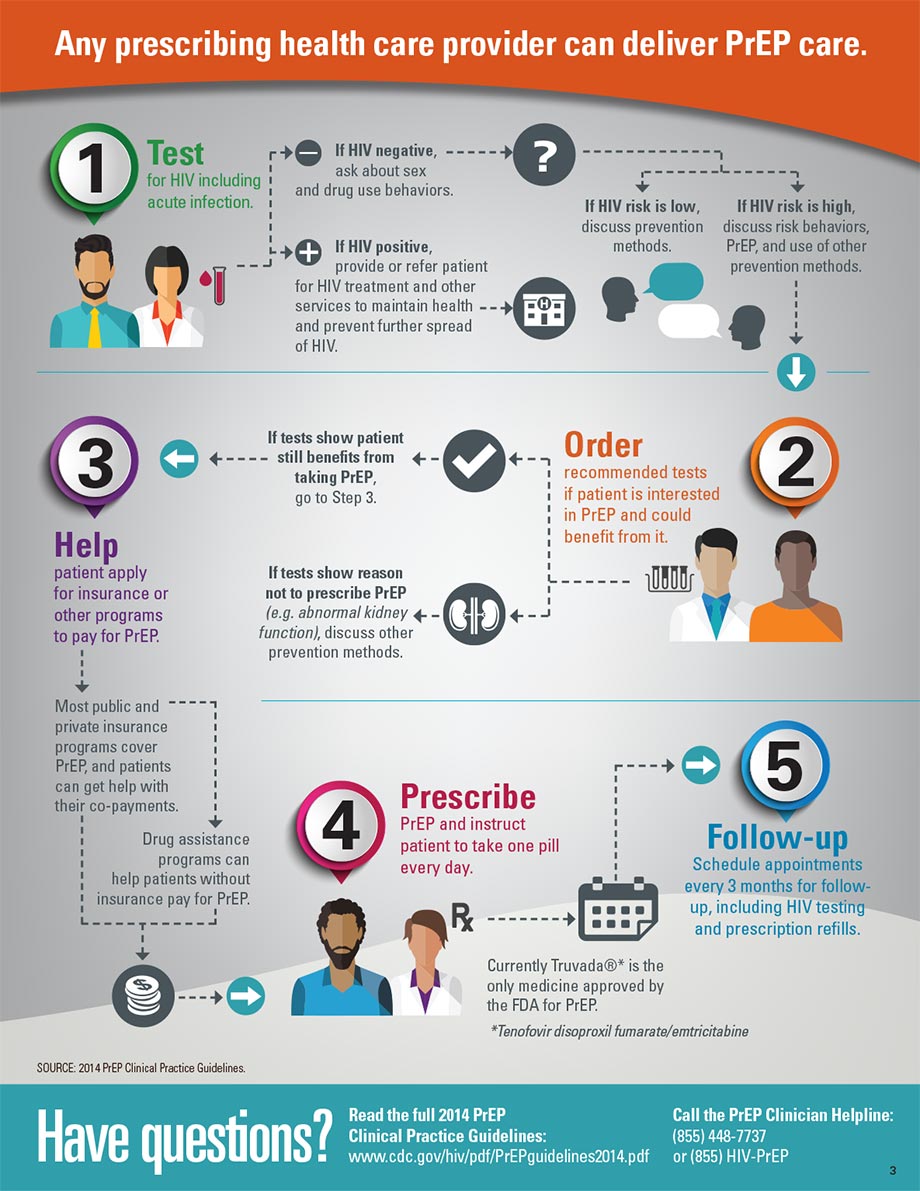
- Test patients for HIV as a regular part of medical care. Discuss HIV risks and continued use of prevention methods, including condom use, with all patients.
- Follow the 2014 PrEP Clinical Practice Guidelines to perform recommended tests and prescribe PrEP to patients without HIV who could benefit.
- Counsel patients who can benefit from PrEP on how to take it every day and help them apply for insurance or other programs to pay for PrEP.
- Schedule appointments for patients using PrEP every 3 months for follow-up, including HIV testing and prescription refills.
*This fact sheet refers to all men who have sex with men (MSM) as gay or bisexual. Sexually active refers to people who have had sex in the past year.

Daily PrEP can reduce the risk of getting HIV from sex by more than 90%.
Daily PrEP can reduce the risk of getting HIV among people who inject drugs by more than 70%.
1 in 3 primary care doctors and nurses haven’t heard about PrEP.
Many people at very high risk for HIV infection are not getting PrEP.
PrEP is for some people at very high risk for getting HIV:
- 1 in 4 sexually active gay and bisexual adult men without HIV who:
- Have an HIV-positive partner, or
- Have multiple partners, a partner with multiple partners, or a partner whose HIV status is unknown and
- Have anal sex without a condom, or
- Recently had a sexually transmitted infection (e.g. syphilis).
- 1 in 5 adults without HIV who inject drugs who:
- Share needles or equipment to inject drugs, or
- Recently went to a drug treatment program (specifically, a methadone, buprenorphine, or suboxone treatment program), or
- Are at risk for getting HIV from sex.
- 1 in 200 sexually active heterosexual adults without HIV who:
- Have an HIV-positive partner, or
- Have multiple partners, a partner with multiple partners, or a partner whose HIV status is unknown and
- Do not always use a condom for sex with people who inject drugs, or
- Are women who do not always use a condom for sex with bisexual men.
About 40,000 HIV infections are diagnosed each year in the US.
Not enough health care providers know about PrEP.
- In 2015, 34% of primary care doctors and nurses had never heard of PrEP (2015 survey).
- All prescribing health care providers can deliver PrEP care, including test for HIV, ask about sex and drug use behaviors to determine their patient’s risk of getting HIV, and prescribe PrEP when indicated.

The Federal government is
- Increasing access to PrEP and other HIV prevention and health care services as recommended in the National HIV/AIDS Strategy for the United States.
- Ensuring coverage of recommended preventive services, such as HIV testing, without cost sharing in most health insurance plans.
- Educating health care providers and people at high risk about PrEP through health department programs, social marketing campaigns, and other training and technical assistance efforts.
- Helping to monitor PrEP use and its effects.
Health care providers can
- Test patients for HIV as a regular part of medical care. Discuss HIV risks and continued use of prevention methods, including condom use, with all patients.
- Follow the 2014 PrEP Clinical Practice Guidelines to perform recommended tests and prescribe PrEP to patients without HIV who could benefit.
- Counsel patients who can benefit from PrEP on how to take it every day and help them apply for insurance or other programs to pay for PrEP.
- Schedule appointments for patients using PrEP every 3 months for follow-up, including HIV testing and prescription refills.
State and local health departments and community-based organizations can
- Raise awareness about PrEP use, train health care providers, and develop policies and procedures that will increase access to PrEP.
- Monitor PrEP use among those at highest risk for HIV.
- Educate people about risky sexual and drug use behaviors and ways to reduce their risk, including PrEP and how to get it.
Everyone can
- Get tested for HIV and know their status.
- Learn how HIV is transmitted and how it can be prevented.
- Talk to their health care providers about HIV risk and ways to prevent it, including PrEP, condom use, abstinence, drug treatment, and HIV treatment for people with HIV.
Everyone taking PrEP can
Issue Details
- Vital Signs Issue details: Estimated Percentages and Numbers of Adults with Indications for Preexposure Prophylaxis to Prevent HIV Acquisition — United States, 2015, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR)
- Vital Signs Issue details: Increased Medicaid Prescriptions for Preexposure Prophylaxis Against HIV infection — New York, 2012–2015, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR)
- Vital Signs – Daily Pill Can Prevent HIV [PODCAST – 1:15 minutes]
- Vital Signs – Daily Pill Can Prevent HIV [PSA – 0:60 seconds]
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
- HIV Basics
- HIV Among Gay and Bisexual Men
- HIV and Injection Drug Use
- Act Against AIDS