Vital Signs: Zika Virus
Vital Signs: Zika Virus
Protecting Pregnant Women and Babies
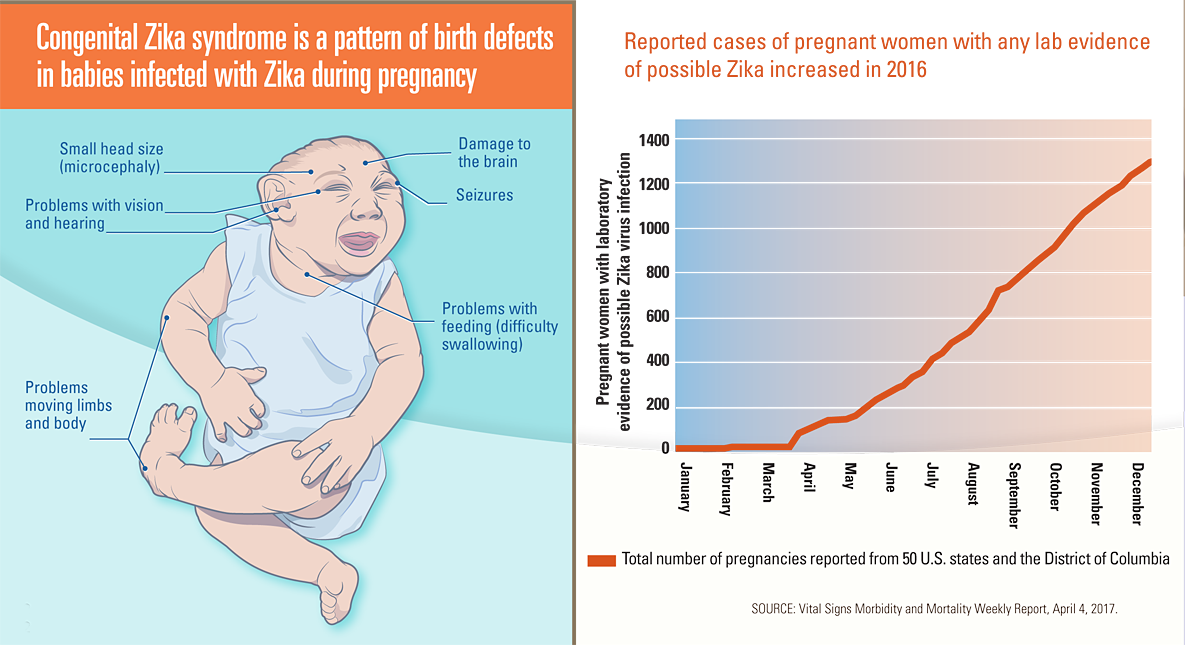
Congenital Zika syndrome is a pattern of birth defects in babies infected with Zika during pregnancy.
- Small head size (microcephaly), problems with vision and hearing, problems moving limbs and body, damage to the brain, seizures, and problems with feeding (difficulty swallowing) are the birth defects related to congenital Zika syndrome
| Week | Month | Total number of pregnancies with laboratory evidence of possible Zika virus infection reported from 50 states and DC |
| 1 | January 2016 | 0 |
| 2 | January | 0 |
| 3 | January | 0 |
| 4 | January | 0 |
| 5 | February | 0 |
| 6 | February | 0 |
| 7 | February | 9 |
| 8 | February | 9 |
| 9 | March | 9 |
| 10 | March | 9 |
| 11 | March | 11 |
| 12 | March | 11 |
| 13 | March | 11 |
| 14 | April | 73 |
| 15 | April | 92 |
| 16 | April | 113 |
| 17 | April | 132 |
| 18 | May | 134 |
| 19 | May | 135 |
| 20 | May | 153 |
| 21 | May | 187 |
| 22 | June | 222 |
| 23 | June | 244 |
| 24 | June | 271 |
| 25 | June | 290 |
| 26 | June | 326 |
| 27 | July | 346 |
| 28 | July | 400 |
| 29 | July | 430 |
| 30 | July | 478 |
| 31 | August | 507 |
| 32 | August | 527 |
| 33 | August | 579 |
| 34 | August | 630 |
| 35 | September | 711 |
| 36 | September | 731 |
| 37 | September | 768 |
| 38 | September | 803 |
| 39 | September | 835 |
| 40 | October | 879 |
| 41 | October | 907 |
| 42 | October | 967 |
| 43 | October | 1012 |
| 44 | November | 1057 |
| 45 | November | 1088 |
| 46 | November | 1124 |
| 47 | November | 1154 |
| 48 | December | 1182 |
| 49 | December | 1229 |
| 50 | December | 1253 |
| 51 | December | 1285 |
| 52 | December | 1297 |
SOURCE: Vital Signs Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, April 4, 2017.
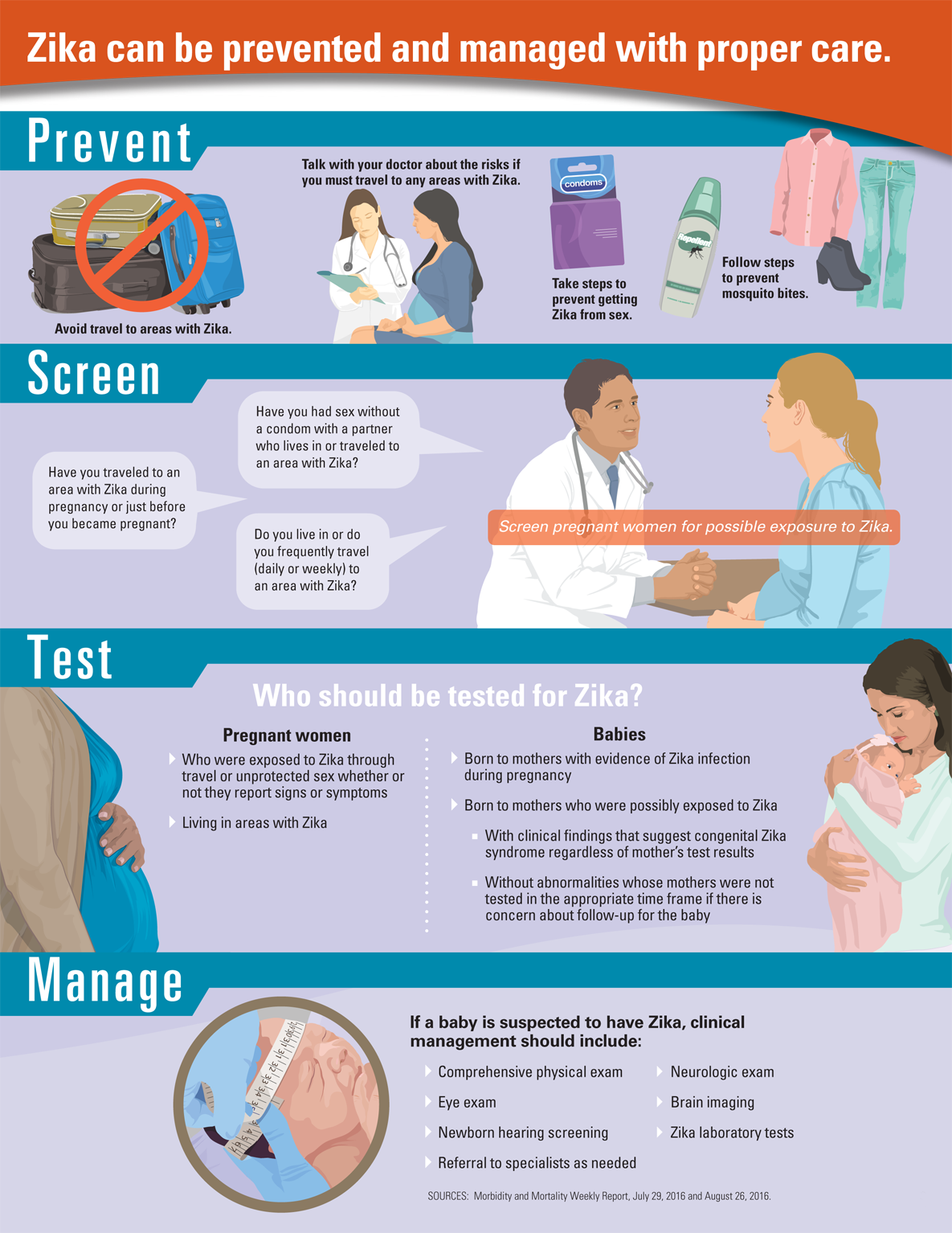
Zika can be prevented and managed with proper care.
Prevent
- Avoid travel to areas with Zika.
- Talk with your doctor about the risks if you must travel to any areas with Zika.
- Take steps to prevent getting Zika from sex.
- Follow steps to prevent mosquito bites.
Screen
- Screen pregnant women for possible exposure to Zika:
- Have you traveled to an area with Zika during pregnancy or just before you became pregnant?
- Have you had sex without a condom with a partner who lives in or traveled to an area with Zika?
- Do you live in or do you frequently travel (daily or weekly) to an area with Zika?
Test
Who should be tested for Zika?
Pregnant women
- Who were exposed to Zika through travel or unprotected sex whether or not they report signs or symptoms
- Living in areas with Zika
Babies
- Born to mothers with evidence of Zika infection during pregnancy
- Born to mothers who were possibly exposed to Zika
- With clinical findings that suggest congenital Zika syndrome regardless of mother’s test results
- Without abnormalities whose mothers were not tested in the appropriate time frame if there is concern about follow-up for the baby
Manage
If a baby is suspected to have Zika, clinical management should include:
- Comprehensive physical exam
- Neurologic exam
- Eye exam
- Brain imaging
- Newborn hearing screening
- Zika laboratory tests
- Referral to specialists as needed
SOURCES: Vital Signs Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, July 29, 2016 and August 26, 2016.
