What is Ethylene Glycol?
Course: WB 4342
CE Original Date: March 20, 2020
CE Renewal Date: March 20, 2022
CE Expiration Date: March 20, 2024
Download Printer-Friendly version [PDF – 954 KB]
After completing this section, you will be able to describe the properties of ethylene glycol.
Ethylene glycol is a liquid that is
- clear,
- colorless,
- odorless, and
- sweet tasting.
Ethylene glycol has low vapor pressures at room temperature and, therefore, low potential for significant inhalation exposure.
Its chemical structure is HOCH2CH2OH.
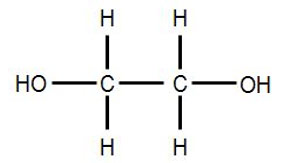
Common synonyms for ethylene glycol include
- ethylene alcohol,
- glycol alcohol,
- glycol,
- 1,2-dihydroxyethane, and
- 1,2-ethanediol.
Ethylene glycol
- dissolves in water and alcohol,
- can hold large amounts of heat before boiling,
- lowers the freezing point of water, and
- absorbs twice its weight in water.
Ethylene glycol is widely used as antifreeze (concentration range: 80%–99%) or de-icing solutions (concentration range: 3%–40%) for cars, boats, and aircraft. It is also used in the chemical synthesis of plastics, films, and solvents. It can be found in many consumer products, including solvents, paints, and coolants (concentration range: 20%–95%) (Caravati et al. 2005).
Ethylene glycol poisoning is a relatively common occurrence worldwide. Thousands of cases of poisoning and some fatal cases occur annually in the United States alone (AAPCC 2016).
Systemic ethylene glycol toxicity can occur following ingestion. The toxic metabolic by-products of ethylene glycol metabolism cause a buildup of acids in the blood (metabolic acidosis). These toxic substances first affect the central nervous system, then the cardiopulmonary system, and finally can cause renal failure. Untreated ethylene glycol poisoning can be fatal (NIOSH 2014). The lethal oral dose in humans is approximately 1.4 mL/kg of pure ethylene glycol (Brent 2001).
- Ethylene glycol is widely used in antifreeze and in de-icing solutions for cars, boats, and aircraft.
- Untreated ethylene glycol poisoning can be fatal.
To review relevant content, see “Definition”, “Properties”, and “Toxicity” in this section.