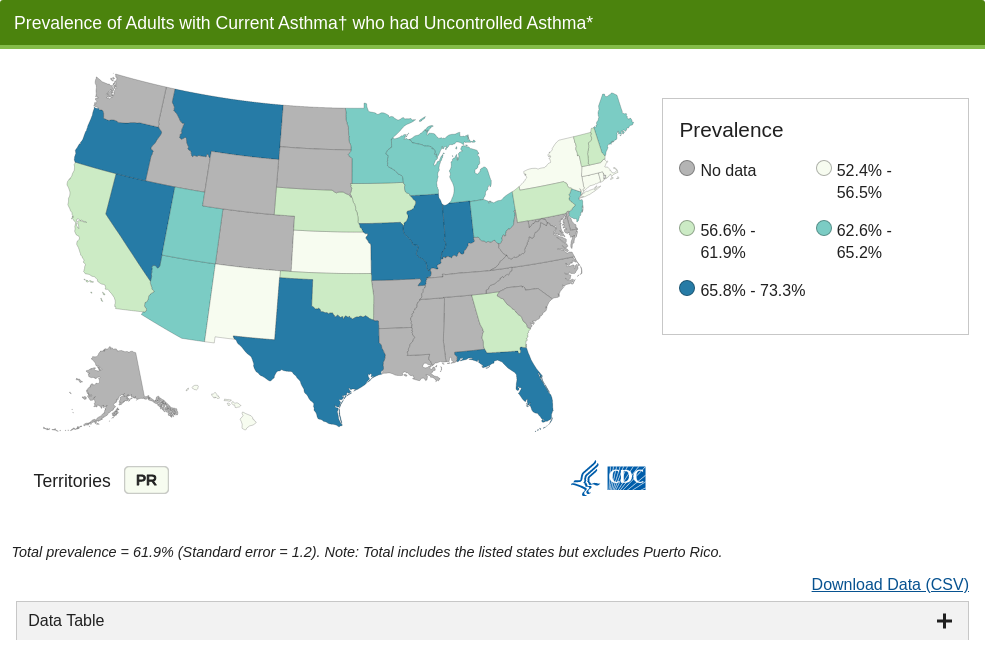
Uncontrolled Asthma among Adults, 2016
More than 60% of adults with current asthma had uncontrolled asthma
Controlled asthma has a minimal impact on everyday living. Uncontrolled asthma with frequent and intense episodes of symptoms can have a significant cost to families and society because it may relate to an increased risk of an emergency department visit, hospitalization, and work and school absenteeism. Asthma control was classified as well-controlled or uncontrolled based on the national asthma guidelines.*
A total of 61.9% of adults with current asthma† had uncontrolled asthma. The level of asthma control varies by demographic characteristics but differences were not significant. It also varies by state but does not seem to follow a specific geographic pattern. The percentage with uncontrolled asthma for adults ranged from 52.4% in Massachusetts to 73.3% in Missouri. (See maps above).
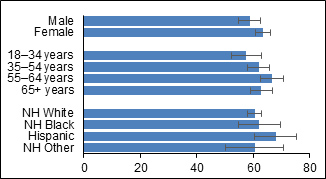
Abbreviation: NH, Non-Hispanic
| Characteristic | Prevalence (percent) |
95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 58.7 | 54.7 – 62.5 |
| Female | 63.5 | 60.7 – 66.3 |
| 18-34 years | 57.6 | 52.3 – 62.6 |
| 35-54 years | 61.9 | 57.9 – 65.7 |
| 55-64 years | 66.6 | 62.5 – 70.4 |
| 65+ years | 62.9 | 58.9 – 66.7 |
| NH White | 60.6 | 58.1 – 63.0 |
| NH Black | 62.2 | 54.7 – 69.2 |
| Hispanic | 68.0 | 60.2 – 75.0 |
| NH Other | 60.5 | 49.9 – 70.1 |
**Includes listed states but excludes Puerto Rico
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)—Adult Asthma Call-back Survey Data, 2016
*National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert panel report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma, 2007. Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/asthma/asthgdln.pdf.
†Includes persons who answered “yes” to the questions: “Have you ever been told by a doctor, nurse, or other health professional that you had asthma?” and “Do you still have asthma?”