Education
PAGE 9 of 19
‹View Table of Contents
Among the male Registry participants who were 25 years of age or older, 2% of hemophilia A participants and 7% of hemophilia B participants had less than a high-school education. Thirty-two percent of hemophilia A participants and 31% of hemophilia B participants were high-school graduates or had passed their General Educational Development (GED) exam. Fifty-eight percent of those with hemophilia A and 53% of those with hemophilia B had more than a high-school education. Education was other or unknown for 9% of hemophilia A participants and 10% for hemophilia B participants (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Highest education among male Registry participants, ages 25 years and older, with hemophilia A or B
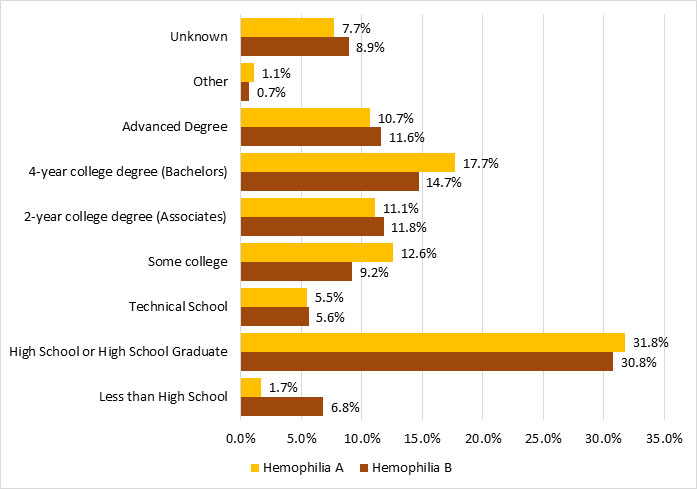
| Hemophilia A | Hemophilia B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education Level | n | % | n | % |
| Less than high school | 49 | 1.7% | 57 | 6.8% |
| High School or High School Graduate | 901 | 31.8% | 258 | 30.8% |
| Technical School | 156 | 5.5% | 47 | 5.6% |
| Some College | 356 | 12.6% | 77 | 9.2% |
| 2-year college degree (Associates) | 314 | 11.1% | 99 | 11.8% |
| 4-year college degree (Bachelors) | 502 | 17.7% | 123 | 14.7% |
| Advanced Degree | 302 | 10.7% | 97 | 11.6% |
| Other | 32 | 1.1% | 6 | 0.7% |
| Unknown | 217 | 7.7% | 75 | 8.9% |
Pages in this Report
- Highlights & Acknowledgements
- Background
- Methods
- Geographic Distribution of Registry Participants
- Diagnosis & Severity
- Registry Characteristics
- Age
- Race/Ethnicity
- ›Education
- Weight Status
- Health Insurance Coverage
- Viral and Vaccination History
- Healthcare Utilization and Absenteeism
- Family History and Genetic Mutation
- Complications
- Treatment
- Procedures and Comorbid Conditions
- Technical Notes
- Participating HTCs