Treatment
‹View Table of Contents
Treatment Regimen and Hemophilia Severity
The majority of male Registry participants with mild or moderate hemophilia A are on an episodic (on-demand) treatment regimen, in which they receive treatment only in response to a bleeding episode (91% and 62%, respectively). Among participants with mild or moderate hemophilia A, continuous prophylaxis is the second most common treatment regimen (4% and 32%, respectively). In contrast, among participants with severe hemophilia A, continuous prophylaxis is the most common treatment regimen, with 77% of participants using this method, followed by episodic or event-based treatment (17%). Among participants with mild, moderate, or severe hemophilia A, event-based, intermittent or short-term prohylaxis, was used by 5%, 6%, and 4%, respectively (Figure 28).
The majority of participants with mild or moderate hemophilia B are on an episodic treatment regimen (91% and 80%, respectively). Continuous prophylaxis is the second most common treatment regimen among participants with mild or moderate hemophilia B (5% and 16%, respectively). Among the male participants with severe hemophilia B, continuous prophylaxis is the most common treatment regimen, followed by episodic or event-based treatment (69% and 25%, respectively). Among participants with hemophilia B, approximately 4% of mild and moderate and 5% of severe used event-based prophylaxis, intermittent or short-term prophylaxis (Figure 29).
Figure 28. Treatment regimen for male Registry participants with hemophilia A, by severity
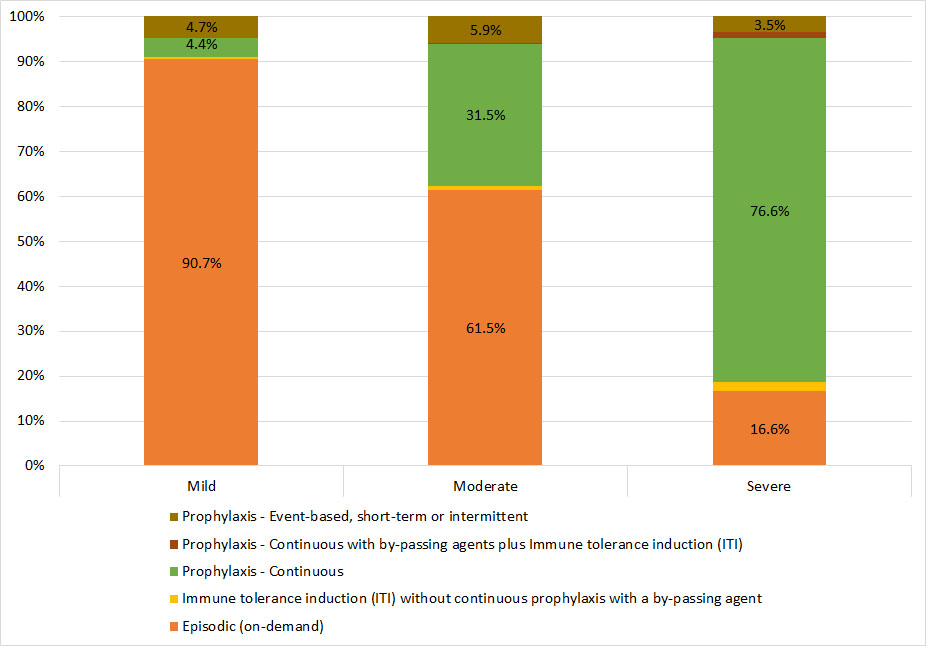
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Episodic (on-demand) | 1517 | 90.7% | 776 | 61.5% | 711 | 16.6% |
| Immune tolerance induction (ITI) without continuous prophylaxis with a by-passing agent | * | * | 11 | 0.9% | 87 | 2.0% |
| Prophylaxis – Continuous | 73 | 4.4% | 397 | 31.5% | 3289 | 76.6% |
| Prophylaxis – Continuous with by-passing agents plus Immune tolerance induction (ITI) | * | * | * | * | 59 | 1.4% |
| Prophylaxis – Event-based, short-term or intermittent | 78 | 4.7% | 74 | 5.9% | 150 | 3.5% |
* Counts less than six have been suppressed to protect patient confidentiality
Figure 29. Treatment regimen for male Registry participants with hemophilia B, by severity
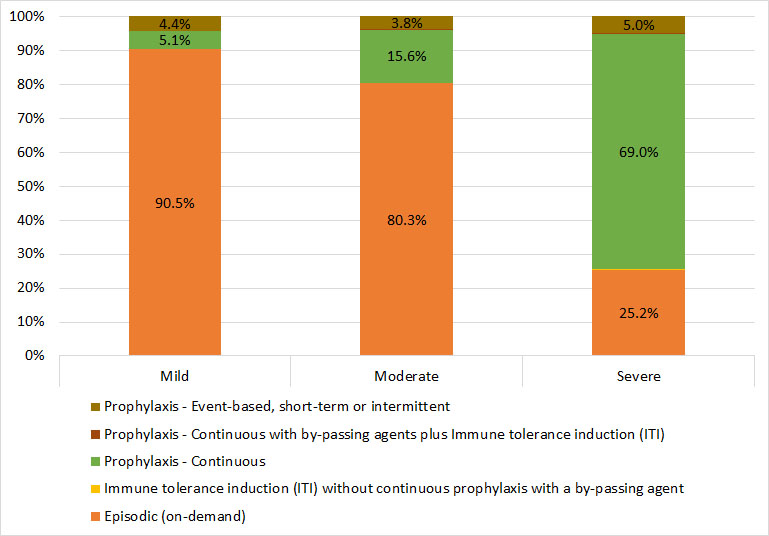
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Episodic (on-demand) | 392 | 90.5% | 572 | 80.3% | 187 | 25.2% |
| Immune tolerance induction (ITI) without continuous prophylaxis with a by-passing agent | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| Prophylaxis – Continuous | 22 | 5.1% | 111 | 15.6% | 511 | 69.0% |
| Prophylaxis – Continuous with by-passing agents plus Immune tolerance induction (ITI) | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| Prophylaxis – Event-based, short-term or intermittent | 19 | 4.4% | 27 | 3.8% | 37 | 5.0% |
* Counts less than six have been suppressed to protect patient confidentiality
Treatment Products and Age
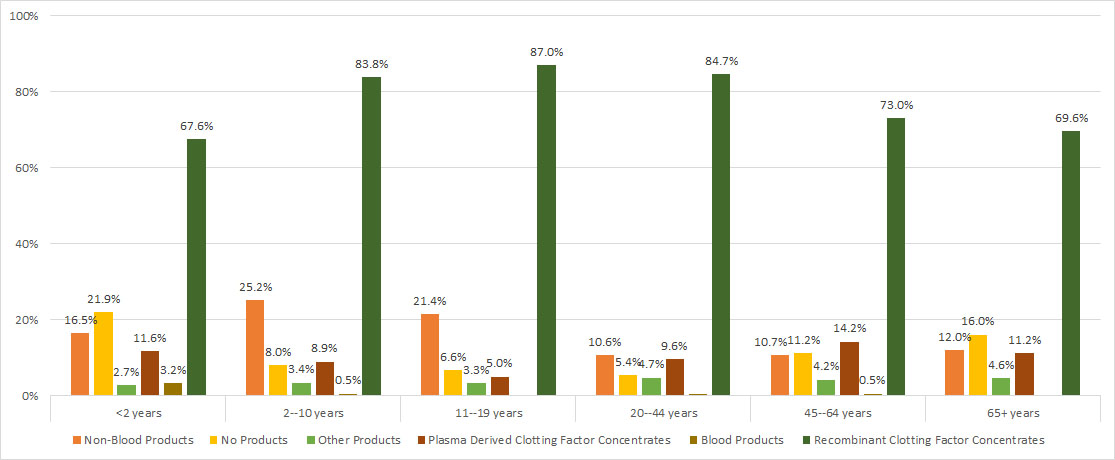
Recombinant clotting factor concentrates were the most commonly used medication, regardless of age group; also common among the younger age groups were non-plasma products.
Figure 30. Product usage among male Registry participants with hemophilia, by age
| <2 years | 2–10 years | 11–19 years | 20–44 years | 45–64 years | 65+ years | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Blood Products | 61 | 16.5% | 539 | 25.2% | 472 | 21.4% | 308 | 10.6% | 128 | 10.7% | 42 | 12.0% |
| No Products | 81 | 21.9% | 172 | 8.0% | 146 | 6.6% | 157 | 5.4% | 134 | 11.2% | 56 | 16.0% |
| Other Products | 10 | 2.7% | 72 | 3.4% | 73 | 3.3% | 138 | 4.7% | 50 | 4.2% | 16 | 4.6% |
| Plasma Derived Clotting Factor Concentrates | 43 | 11.6% | 191 | 8.9% | 110 | 5.0% | 279 | 9.6% | 170 | 14.2% | 39 | 11.2% |
| Blood Products | 12 | 3.2% | 10 | 0.5% | * | * | * | * | 6 | 0.5% | * | * |
| Recombinant Clotting Factor Concentrates | 250 | 67.6% | 1792 | 83.8% | 1917 | 87.0% | 2471 | 84.7% | 872 | 73.0% | 243 | 69.6% |
* Counts less than six have been suppressed to protect patient confidentiality
Pages in this Report
- Highlights & Acknowledgements
- Background
- Methods
- Geographic Distribution of Registry Participants
- Diagnosis & Severity
- Registry Characteristics
- Age
- Race/Ethnicity
- Education
- Weight Status
- Health Insurance Coverage
- Viral and Vaccination History
- Healthcare Utilization and Absenteeism
- Family History and Genetic Mutation
- Complications
- ›Treatment
- Procedures and Comorbid Conditions
- Technical Notes
- Participating HTCs