4.2b Craniorachischisis (Q00.1)
‹View Table of Contents
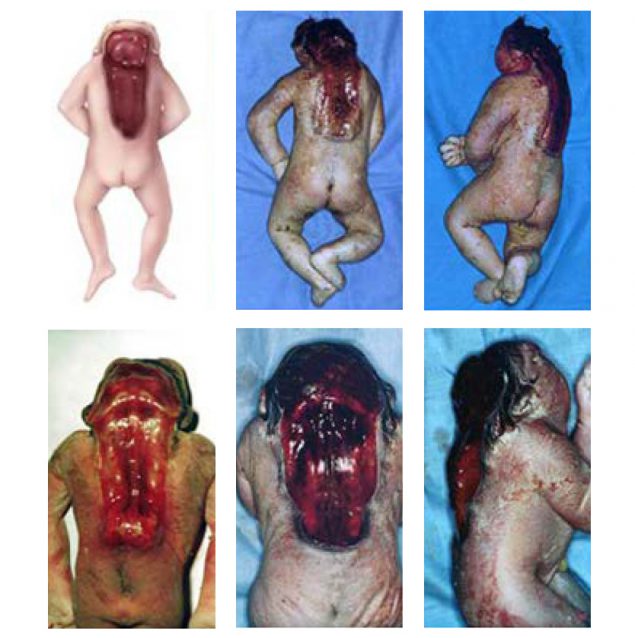
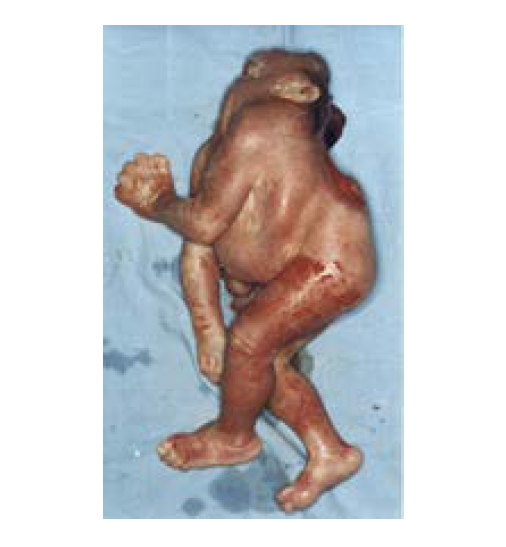
Craniorachischisis is a very serious NTD characterized by the combination of anencephaly (absence of the brain and cranial vault, without skin covering) with a contiguous bony defect of the spine (also without meninges covering the neural tissue – rachischisis) (see Fig. 4.3). Spine involvement can be limited to the cervical spine where it might be difficult to clinically differentiate from holoanencephaly. Rarely, the open defect can extend to the thoracic or even lumbosacral spine (craniorachischisis totalis). Craniorachischisis results from failed closure of the anterior neuropore, but the mechanism leading to failure of closure of the contiguous spine is not well understood. In some infants, there is accompanying retroflexion of the spine, which results in a body habitus resembling another rare NTD, iniencephaly (see Fig. 4.5). Because of the early lethality of this condition, many affected fetuses are either stillborn or result in a termination of pregnancy (if prenatally diagnosed and pregnancy terminations are permitted).
Photograph source: CDC–Beijing Medical University collaborative project.
Relevant ICD-10 codes
Q00.1 Craniorachischisis
Diagnosis
Prenatal. Craniorachischisis is readily diagnosed using ultrasound. However, it can be confused with other defects involving the brain – anencephaly, acrania or amniotic band syndrome. For this reason, a prenatal diagnosis of craniorachischisis should always be confirmed postnatally. When this is not possible (e.g. termination of pregnancy or unexamined fetal death), the programme should have criteria in place to determine whether to accept or not accept a case based solely on prenatal data.
Postnatal. Careful examination of the fetus or newborn can confirm the diagnosis of craniorachischisis and distinguish it from the other rare anomalies that involve the brain, cranium and spine. In craniorachischisis, the eyes are usually normally formed but tend to bulge as a result of the absent frontal portion of the cranial vault, and the neck might appear to be shortened and is sometimes retroflexed. The craniorachischisis lesion is always open and the spinal lesion is always continuous with the anencephaly.
Clinical and epidemiologic notes
Distinguishing craniorachischisis from other abnormalities of the brain and spinal cord is important because these conditions have different causes and associated anomalies. With careful examination, the diagnosis of craniorachischisis is straightforward. Craniorachischisis is a uniformly fatal condition and is often isolated and non-syndromic. However, the co-occurrence of cleft lip and palate, omphalocele, limb defects, cyclopia or trisomy 18 has been reported in some cases, but no robust populationbased studies have been conducted to understand the proportion of isolated cases or associated anomalies. For this reason, it is very important to report all physical findings and obtain good clinical photographs for the expert reviewer. Craniorachischisis is reported to occur more commonly in females.
Craniorachischisis is a rare defect and is most prevalent in countries with an overall high prevalence of NTDs. Because of the rarity of craniorachischisis, studies of non-genetic risk factors are challenging. Presumably the non-genetic risk factors should be similar to that of other NTDs, including pregestational diabetes, obesity, and hyperthermia (e.g. fever) in early pregnancy, and folic acid insufficiency/deficiency. Adequate periconceptional use of folic acid (as a supplement or through fortification) might also prevent craniorachischisis.
Few reports on NTD prevalence specifically mention craniorachischisis. The reported prevalence varies widely, with estimates ranging between 0.1 to 10.7 per 10 000 live births. Craniorachischisis is counted when calculating total NTD prevalence.
Inclusions
Q00.1 Craniorachischisis
Exclusions
Q00.0 Anencephaly, Acrania, acephaly
Q00.2 Iniencephaly
Q00.20 Iniencephaly, open
Q00.21 Iniencephaly, closed
Checklist for high-quality reporting
| Craniorachischisis – Documentation Checklist |
Describe in detail:
Report whether autopsy (pathology) findings are available and if so, report the results. |
Suggested data quality indicators
| Category | Suggested Practices and Quality indicators |
| Description and documentation |
|
| Coding |
|
| Clinical classification |
|
| Prevalence |
|
Table of Contents
- Chapter 4: Diagnosing and Coding Congenital Anomalies
- 4.1 List of Selected External and Internal Congenital Anomalies to Consider for Monitoring
- 4.2 Congenital Malformations of the Nervous System: Neural Tube Defects
- 4.2a Anencephaly
- ›4.2b Craniorachischisis (Q00.1)
- 4.2c Iniencephaly (Q00.2)
- 4.2d Encephalocele (Q01.0–Q01.83, Q01.9)
- 4.2e Spina Bifida (Q05.0–Q05.9)
- 4.3 Congenital Anomalies of the Nervous System: Microcephaly
- 4.4 Congenital Malformations of the Ear
- 4.5a Overview Congenital Heart D: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Confirmation
- 4.5b Common Truncus (Q20.0)
- 4.5c Transposition of Great Arteries (Q20.3)
- 4.5d Tetralogy of Fallot
- 4.5e Pulmonary Valve Atresia (Q22.0)
- 4.5f Tricuspid Valve Atresia (Q22.4)
- 4.5g Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (Q23.4)
- 4.5h Interrupted Aortic Arch (q25.21, Preferred; Also Q25.2, Q25.4)
- 4.6 Orofacial Clefts
- 4.7 Congenital Malformations of the Digestive System
- 4.8 Congenital Malformations of Genital Organs Hypospadias (Q54.0–Q54.9)
- 4.9a Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Talipes Equinovarus (Q66.0)
- 4.9b Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Limb Reduction Defects/Limb Deficiencies
- 4.9c Limb Deficiency Amelia (Q71.0, Q72.0, Q73.0)
- 4.9d Limb Deficiency: Transverse Terminal (Q71.2, Q71.3, Q71.30, Q72.2, Q72.3, Q72.30)
- 4.9e Limb Deficiency: Transverse Intercalary (Q71.1, Q72.1, Q72.4)
- 4.9f Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Preaxial (Tibia, Radius, First Ray) (Q71.31, Q71.4, Q72.31, Q72.5)
- 4.9g Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Postaxial (Fibula, Ulna, Fifth Ray) (Q71.30, Q71.5, Q72.30, Q72.6)
- 4.9h Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Axial Limb Deficiency – Split Hand and Foot (Q71.6, Q72.7)
- 4.10 Abdominal Wall Defects
- 4.11 Chromosomal Abnormalities