4.5h Interrupted Aortic Arch (q25.21, Preferred; Also Q25.2, Q25.4)
‹View Table of Contents
Interrupted aortic arch (IAA) is a structural heart defect characterized anatomically by a discontinuity (interruption) along the aortic arch. Depending on the site of discontinuity, IAA is classified into three types (see Fig. 4.21). Type B is the most common (50–70%), type A is less common (30–45%) and type C is rare.
Fig. 4.21. Interrupted aortic arch
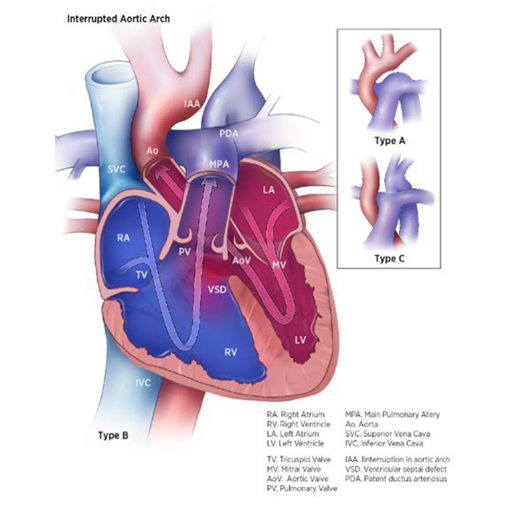
- Type A: The discontinuity is distal to the left subclavian artery (approximately in the same region as coarctation of the aorta).
- Type B (the most common form): The discontinuity is more proximal, between the left carotid and subclavian.
- Type C: The discontinuity is more proximal still, between the brachiocephalic artery and the common carotid artery
Relevant ICD-10 codes
Q25.21 Interruption of aortic arch (preferred)
Q25.2 Atresia of aorta
Q25.4 Other congenital malformations of aorta (heterogeneous; might include interrupted aortic arch)
Diagnosis
Prenatal. IAA is easily missed on the obstetric anomaly scan, though it might be suspected based on discrepancy between the left and right ventricular sizes. Prenatally diagnosed cases should be confirmed postnatally.
Postnatal. Infants can present clinically in the early neonatal period, when the ductus closes, with signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure and systemic hypoperfusion (cardiogenic shock). Newborn screening via pulse oximetry can lead to earlier diagnosis.
Clinical and epidemiologic notes
As noted, an early presentation is heart failure and cardiogenic shock, with rapid clinical deterioration as the ductus closes. Because of right-to-left shunting at the ductus arteriosus, infants might initially show differential oxygen saturation or cyanosis. In type A, the difference in saturation is between the upper and lower limbs, with the lower limbs having lower saturation; in type B, there is a difference in saturation between the left and right arms, with the left arm having lower saturation.
Ventricular septal defect and other intracardiac defects are often present.
The three types of IAA differ in their association with genetic risk factors. For example, deletion 22q11 occurs in 50% or more of cases of type B IAA, and is rare in the other types. Other syndromes that can occur with IAA include CHARGE syndrome (Q30.01).
Environmental risk factors include use of the medication isotretinoin (specifically for type B IAA) and maternal pregestational diabetes.
Birth prevalence of IAA, all types, is approximately 1 in 15 000 births (approximately 0.7 per 10 000 births).
Inclusions
Q25.21 Interruption of aortic arch
Exclusions
Q25.43 Congenital aneurysm of aorta
Q25.44 Congenital dilation of aorta
Q25.45 Double aortic arch
Q25.46 Tortuous aortic arch
Q25.47 Right aortic arch
Q25.48 Anomalous origin of subclavian artery
Checklist for high-quality reporting
| Interrupted Aortic Arch (IAA) – Documentation Checklist |
Describe in detail the clinical and echocardiographic findings:
Look for and document extracardiac birth defects: IAA can occur with genetic syndromes such as deletion 22q11, which is associated with many external and internal anomalies. Report whether specialty consultation(s) was done: Report whether the diagnosis was made by a paediatric cardiologist, and whether the patient was seen by a geneticist. Reportanygenetictestingandresults(e.g. chromosomalstudies, genomicmicroarray, genomicsequencing). |
Suggested data quality indicators
| Category | Suggested Practices and Quality Indicators |
| Description and documentation | Review sample of clinical descriptions for documentation of key elements:
|
| Coding |
|
| Clinical classification |
|
| Prevalence |
|
Table of Contents
- Chapter 4: Diagnosing and Coding Congenital Anomalies
- 4.1 List of Selected External and Internal Congenital Anomalies to Consider for Monitoring
- 4.2 Congenital Malformations of the Nervous System: Neural Tube Defects
- 4.2a Anencephaly
- 4.2b Craniorachischisis (Q00.1)
- 4.2c Iniencephaly (Q00.2)
- 4.2d Encephalocele (Q01.0–Q01.83, Q01.9)
- 4.2e Spina Bifida (Q05.0–Q05.9)
- 4.3 Congenital Anomalies of the Nervous System: Microcephaly
- 4.4 Congenital Malformations of the Ear
- 4.5a Overview Congenital Heart D: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Confirmation
- 4.5b Common Truncus (Q20.0)
- 4.5c Transposition of Great Arteries (Q20.3)
- 4.5d Tetralogy of Fallot
- 4.5e Pulmonary Valve Atresia (Q22.0)
- 4.5f Tricuspid Valve Atresia (Q22.4)
- 4.5g Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (Q23.4)
- ›4.5h Interrupted Aortic Arch (q25.21, Preferred; Also Q25.2, Q25.4)
- 4.6 Orofacial Clefts
- 4.7 Congenital Malformations of the Digestive System
- 4.8 Congenital Malformations of Genital Organs Hypospadias (Q54.0–Q54.9)
- 4.9a Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Talipes Equinovarus (Q66.0)
- 4.9b Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Limb Reduction Defects/Limb Deficiencies
- 4.9c Limb Deficiency Amelia (Q71.0, Q72.0, Q73.0)
- 4.9d Limb Deficiency: Transverse Terminal (Q71.2, Q71.3, Q71.30, Q72.2, Q72.3, Q72.30)
- 4.9e Limb Deficiency: Transverse Intercalary (Q71.1, Q72.1, Q72.4)
- 4.9f Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Preaxial (Tibia, Radius, First Ray) (Q71.31, Q71.4, Q72.31, Q72.5)
- 4.9g Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Postaxial (Fibula, Ulna, Fifth Ray) (Q71.30, Q71.5, Q72.30, Q72.6)
- 4.9h Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Axial Limb Deficiency – Split Hand and Foot (Q71.6, Q72.7)
- 4.10 Abdominal Wall Defects
- 4.11 Chromosomal Abnormalities