Encephalocele
Encephalocele is an NTD characterized by a pedunculated or sessile cystic, skin-covered lesion protruding through a defect in the cranium (skull bone). Encephaloceles can contain herniated meninges and brain tissue (encephalocele or meningoencephalocele) or only meninges (cranial meningocele).
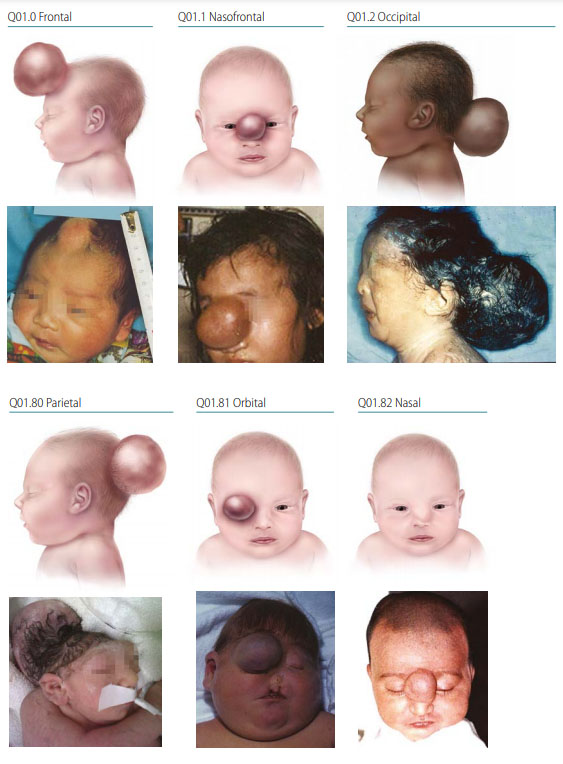
Photograph sources: CDC–Beijing Medical University collaborative project; Dr Jaime Frias
- Location – the midline defect will vary in location and size; the most common location is occipital (~74%), followed by parietal (13%).
- Covering – encephalocele is skin covered (unless a rupture has occurred).
- Herniation – may contain meninges and brain tissue (encephalocele) or meninges only (cranial meningocele).
Diagnosis
Prenatal. Encephalocele might be diagnosed prenatally using ultrasound but should always be confirmed postnatally. Use programme rules (SOPs) to decide whether to accept or not accept prenatal diagnoses without postnatal confirmation (e.g. in cases of termination of pregnancy or unexamined fetal death).
Postnatal. The newborn examination, x-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) confirm the diagnosis and will distinguish it from the other anomalies that may involve the brain and cranium.
Clinical and epidemiologic notes
- Polydactyly and/or renal anomalies.
- May co-occur with Dandy-Walker malformation or Chiari malformation.
- Can occur with many single genes disorders (e.g., Meckel-Gruber syndrome) and with some chromosomal anomalies (e.g., trisomy 13, trisomy 18).
- Always look for additional anomalies and syndromes.
- Note encephalocele location and size, and document if meninges and brain are herniated.
- Check if amniotic bands are mentioned – encephalocele might be confused with the amniotic band spectrum. The occurrence of other findings (facial schisis, limb and ventral wall anomalies, bands) points towards the diagnosis of amniotic band spectrum.
Checklist for high-quality reporting
| Encephalocele – Documentation Checklist |
Describe in detail:
Take and report photographs: Show clearly the cranial lesion; can be crucial for review Describe evaluations to find or rule out related and associated anomalies:
Report whether autopsy (pathology) findings are available and if so, report the results. |