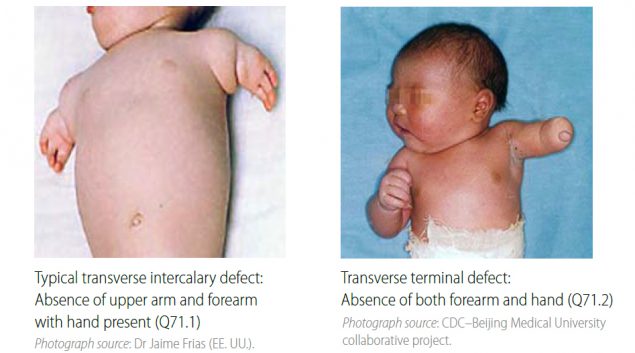
4.9e Limb Deficiency: Transverse Intercalary (Q71.1, Q72.1, Q72.4)
‹View Table of Contents
Fig. 4.38. Transverse intercalary
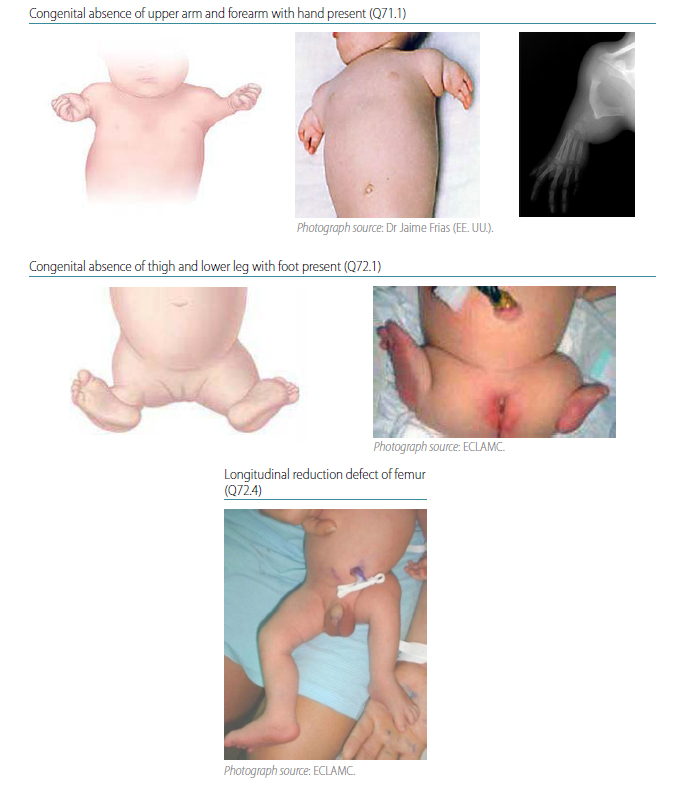
Transverse intercalary limb deficiencies are characterized by the absence of proximal or middle segments of a limb with all or part of the distal segment present. Radiographs are strongly recommended to confirm the condition and characterize the bony anatomy.
Relevant ICD-10 codes
Q71.1 Congenital absence of upper arm and forearm with hand present
Phocomelia of upper limb
Q72.1 Congenital absence of thigh and lower leg with foot present
Phocomelia of lower limb
Q72.4 Longitudinal reduction defect of femur
Proximal femoral focal deficiency
Note:
Avoid using the generic Q71, Q72 or Q73 codes for intercalary limb deficiencies. These generic codes include other limb deficiencies.
Diagnosis
Prenatal. Transverse intercalary limb deficiency can be suspected prenatally, but is easily missed or misdiagnosed. Cases identified or suspected prenatally should be confirmed postnatally before inclusion in the surveillance programme. When this is not possible (e.g. termination of pregnancy or unexamined fetal death), the programme should have criteria in place to determine whether to accept or not accept a case based solely on prenatal data.
Postnatal. The newborn examination confirms the diagnosis of intercalary limb deficiency and distinguishes it from other limb deficiencies (such as amelia). A careful clinical examination and documentation, aided by imaging (photos and radiographs), are essential for an accurate and complete diagnosis.
Clinical and epidemiologic notes
Typical intercalary deficiencies present with absence of all limb bones proximal to a normal or malformed hand or foot which attaches directly to the trunk. Atypical intercalary deficiencies present with absence of humerus or femur, or both radius-ulna (tibia-fibula) with normal or malformed hand or foot. Distinguishing intercalary defects from other limb reduction defects is important because these conditions have different causes and disease associations. With careful clinical and radiological examination, the diagnosis of intercalary limb deficiencies is possible.
Note that the English translation for the term “phocomelia” is considered pejorative and should not be used. Translation from Latin to English alludes to the shape of the limb resembling that of a flipper on a seal.
About half of transverse intercalary limb deficiency cases are isolated. Most of the remaining cases have multiple congenital anomalies. A small proportion of cases are syndromic. Syndromes with intercalary limb deficiencies include Roberts syndrome; in its most severe form, thrombocytopenia absent radius (TAR) syndrome can have intercalary limb deficiencies.
A teratogen that can cause intercalary limb deficiencies is thalidomide. Maternal pregestational diabetes has been associated with femoral hypoplasia-unusual facies syndrome (now more commonly called femoral-facial syndrome). This condition is characterized by unilateral or bilateral deficiency of femurs, with variable deficiencies of other long bones.
The prevalence of intercalary limb deficiencies is around 0.45 per 10 000 births.
Inclusions
Q71.1 Congenital absence of upper arm and forearm with hand present
Phocomelia of upper limb
Q72.1 Congenital absence of thigh and lower leg with foot present
Phocomelia of lower limb
Q72.4 Longitudinal reduction defect of femur
Proximal femoral focal deficiency
Related codes
Q87.25 Thrombocytopenia absent radius syndrome
Q86.82 Congenital malformations due to thalidomide
Exclusions
Q71.0 Congenital complete absence of upper limb(s); amelia of upper limb
Q71.2 Congenital absence of both forearm and hand
Q71.3 Congenital absence of hand and finger(s)
Q71.30 Congenital absence of finger(s)
Q72.0 Congenital complete absence of lower limb(s); amelia of lower limb
Q72.2 Congenital absence of both lower leg and foot
Q72.3 Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)
Q72.30 Congenital absence or hypoplasia of toe(s) with remainder of foot intact
Q73.0 Congenital absence of unspecified limb(s)
Checklist for high-quality reporting
| Intercalary Defects – Documentation Checklist |
Describe in detail, including:
|
Suggested data quality indicators
| Category | Suggested Practices and Quality indicators |
| Description and documentation | Review sample for documentation of key descriptors:
|
| Coding |
|
| Clinical classification |
|
| Prevalence |
|
| Key visuals | Distinguishing intercalary defects from transverse terminal defects (side-by-side comparison):
|
Table of Contents
- Chapter 4: Diagnosing and Coding Congenital Anomalies
- 4.1 List of Selected External and Internal Congenital Anomalies to Consider for Monitoring
- 4.2 Congenital Malformations of the Nervous System: Neural Tube Defects
- 4.2a Anencephaly
- 4.2b Craniorachischisis (Q00.1)
- 4.2c Iniencephaly (Q00.2)
- 4.2d Encephalocele (Q01.0–Q01.83, Q01.9)
- 4.2e Spina Bifida (Q05.0–Q05.9)
- 4.3 Congenital Anomalies of the Nervous System: Microcephaly
- 4.4 Congenital Malformations of the Ear
- 4.5a Overview Congenital Heart D: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Confirmation
- 4.5b Common Truncus (Q20.0)
- 4.5c Transposition of Great Arteries (Q20.3)
- 4.5d Tetralogy of Fallot
- 4.5e Pulmonary Valve Atresia (Q22.0)
- 4.5f Tricuspid Valve Atresia (Q22.4)
- 4.5g Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (Q23.4)
- 4.5h Interrupted Aortic Arch (q25.21, Preferred; Also Q25.2, Q25.4)
- 4.6 Orofacial Clefts
- 4.7 Congenital Malformations of the Digestive System
- 4.8 Congenital Malformations of Genital Organs Hypospadias (Q54.0–Q54.9)
- 4.9a Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Talipes Equinovarus (Q66.0)
- 4.9b Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Limb Reduction Defects/Limb Deficiencies
- 4.9c Limb Deficiency Amelia (Q71.0, Q72.0, Q73.0)
- 4.9d Limb Deficiency: Transverse Terminal (Q71.2, Q71.3, Q71.30, Q72.2, Q72.3, Q72.30)
- ›4.9e Limb Deficiency: Transverse Intercalary (Q71.1, Q72.1, Q72.4)
- 4.9f Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Preaxial (Tibia, Radius, First Ray) (Q71.31, Q71.4, Q72.31, Q72.5)
- 4.9g Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Postaxial (Fibula, Ulna, Fifth Ray) (Q71.30, Q71.5, Q72.30, Q72.6)
- 4.9h Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Axial Limb Deficiency – Split Hand and Foot (Q71.6, Q72.7)
- 4.10 Abdominal Wall Defects
- 4.11 Chromosomal Abnormalities