4.9d Limb Deficiency: Transverse Terminal (Q71.2, Q71.3, Q71.30, Q72.2, Q72.3, Q72.30)
‹View Table of Contents
Fig. 4.37. Transverse terminal
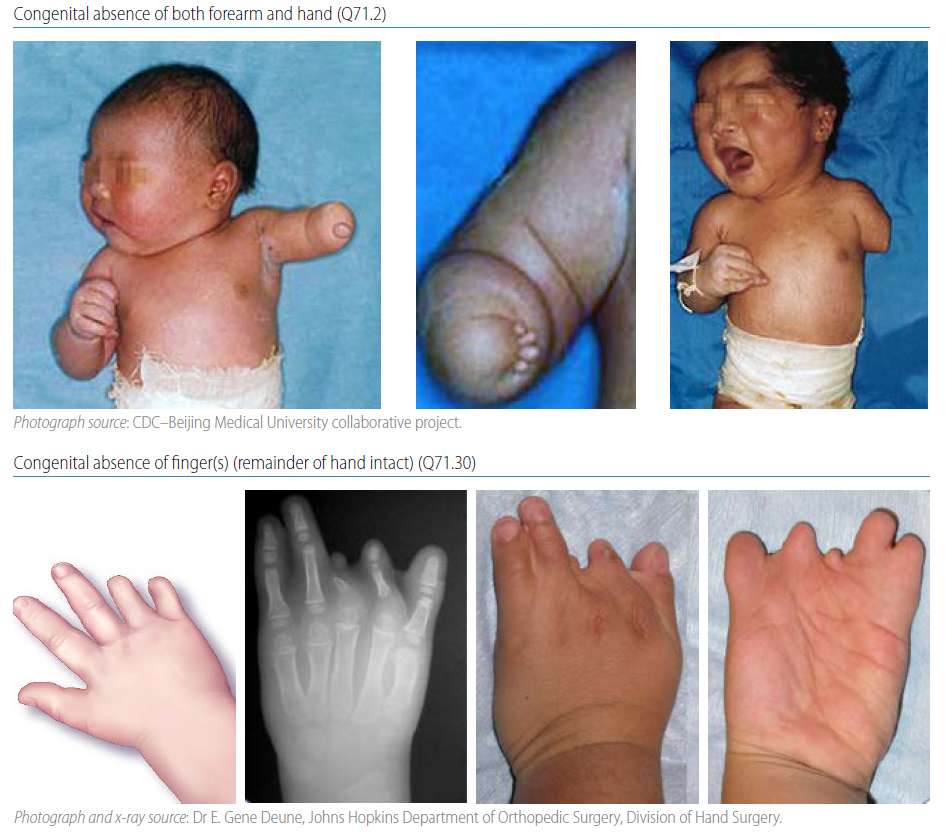
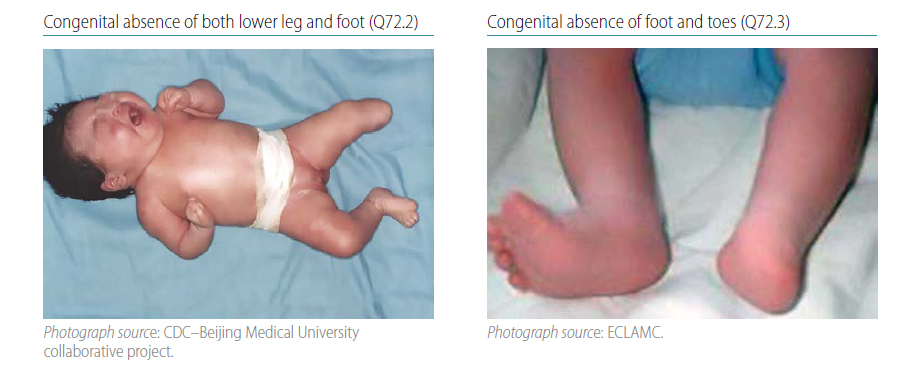
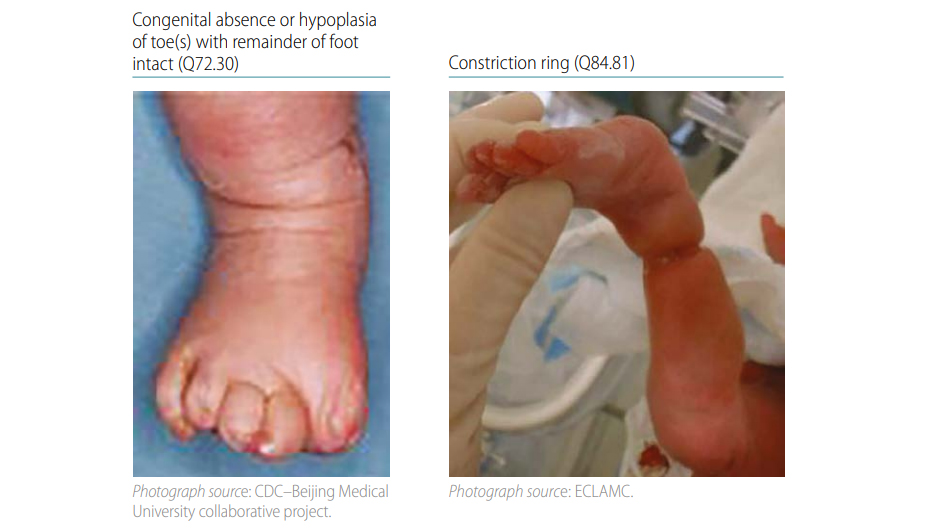
Terminal transverse limb deficiency is a congenital anomaly that appears as an “amputation” of an arm, leg or digit/toe. The limb is missing the terminal (distal) segment(s), with preservation of all the segment(s) proximal to the missing segment. For example, if fingers are missing, the remainder of the hand, forearm and arm are all still present (small nubbins may be present terminally; see clinical description below). Radiographs are strongly recommended and can be essential to confirm the condition and characterize the bony anatomy.
Relevant ICD-10 codes
Q71.2 Congenital absence of both forearm and hand
Q71.3 Congenital absence of hand and finger(s)
Q71.30 Congenital absence of finger(s)
Q72.2 Congenital absence of both lower leg and foot
Q72.3 Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)
Q72.30 Congenital absence or hypoplasia of toe(s) with remainder of foot intact
Note:
Avoid using the generic Q71, Q72 or Q73 to code transverse terminal limb deficiencies. These generic codes include other limb deficiencies.
Diagnosis
Prenatal. Terminal transverse limb deficiencies might be diagnosed or strongly suspected prenatally. However, they can be missed or misdiagnosed as one of the other limb deficiencies. For these reasons, a prenatal diagnosis should always be confirmed postnatally. When this is not possible (e.g. termination of pregnancy or unexamined fetal death), the programme should have criteria in place to determine whether to accept or not accept a case based solely on prenatal data.
Postnatal. The newborn examination confirms the diagnosis of terminal transverse limb deficiency and distinguishes it from other limb deficiencies. It is important to underline the importance of a detailed examination and documentation, including imaging (photographs and radiographs).
Clinical and epidemiologic notes
Distinguishing terminal transverse defects from other limb deficiencies is important because these conditions have different causes and associated anomalies. With careful clinical and radiological examination, transverse terminal limb deficiencies can be reliably diagnosed.
Terminal transverse deficiency represents a wide spectrum of limb abnormalities, with partial amputation of the distal limb. The terminal partial amputation can involve digits, toes, forearm, arm, leg or thigh. Transverse deficiencies are the most common limb deficiencies, most often caused by the early amnion rupture disruption sequence, also referred to as amniotic bands. The damage from anamniotic band can range from constriction of a limb to hypoplasia of digits with syndactyly, rudimentary digits, and absence of the limb distally from the site of the in-utero amputation. Amniotic bands can also cause disruptions at other sites, such as the face and body wall. Typically, the transverse deficiencies are not symmetric.
In cases involving the hand, there can be small soft tissue “nubbins” arranged in a pattern suggesting rudimentary digits. Most cases of terminal transverse deficiency occur sporadically and as an isolated abnormality involving a single limb in an otherwise healthy individual.
The risk of transverse terminal limb deficiencies increases with the use of misoprostol in failed abortions. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) at 9 weeks or earlier has been associated with transverse terminal limb deficiencies. Among genetic syndromes, consider Adams–Oliver syndrome if the terminal transverse limb defect is associated with aplasia cutis congenita and/or CHD.
From an epidemiologic perspective, transverse terminal limb deficiencies are the most frequent type of limb deficiency, with a birth prevalence of approximately 2.5 per 10 000 births.
Inclusions
Q71.2 Congenital absence of both forearm and hand
Q71.3 Congenital absence of hand and finger(s)
Q71.30 Congenital absence of finger(s)
Q72.2 Congenital absence of both lower leg and foot
Q72.3 Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)
Q72.30 Congenital absence or hypoplasia of toe(s) with remainder of foot intact
Related codes
Q89.81 Limb-body wall complex
Q79.80 Amniotic band
Q84.81 Constriction ring
Exclusions
Q71.0 Congenital complete absence of upper limb(s); amelia of upper limb
Q71.1 Congenital absence of upper arm and forearm with hand present
Phocomelia of upper limb
Q72.0 Congenital complete absence of lower limb(s); amelia of lower limb
Q72.1 Congenital absence of thigh and lower leg with foot present
Phocomelia of lower limb
Q72.4 Longitudinal reduction defect of femur
Proximal femoral focal deficiency
Q73.0 Congenital absence of unspecified limb(s)
Q71.6 Congenital cleft hand
Q72.7 Split foot
Checklist for high-quality reporting
| Transverse Terminal Defects – Documentation Checklist |
Describe in detail, including:
|
Suggested data quality indicators
| Category | Suggested Practices and Quality indicators |
| Description and documentation | Review sample for documentation of key descriptors:
|
| Coding |
|
| Clinical classification |
|
| Prevalence |
|
| Key visuals | Distinguishing transverse terminal defects from longitudinal axial defects and amelia (side-by-side comparison):
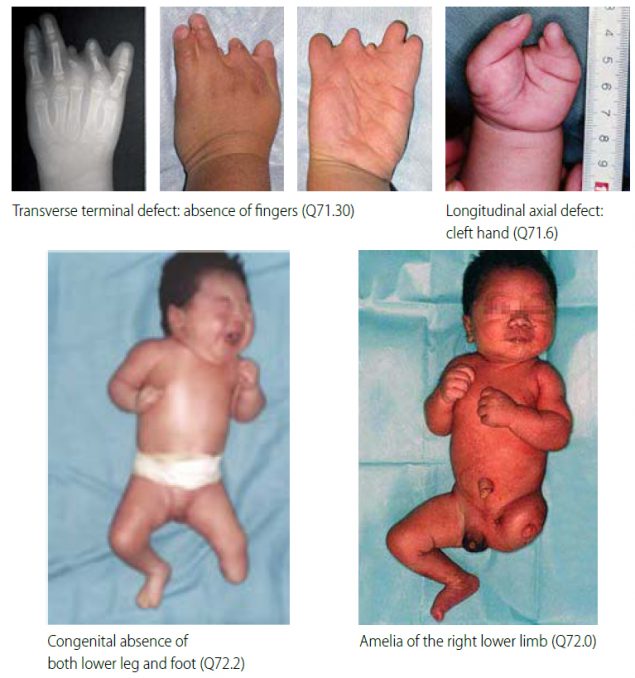
|
Table of Contents
- Chapter 4: Diagnosing and Coding Congenital Anomalies
- 4.1 List of Selected External and Internal Congenital Anomalies to Consider for Monitoring
- 4.2 Congenital Malformations of the Nervous System: Neural Tube Defects
- 4.2a Anencephaly
- 4.2b Craniorachischisis (Q00.1)
- 4.2c Iniencephaly (Q00.2)
- 4.2d Encephalocele (Q01.0–Q01.83, Q01.9)
- 4.2e Spina Bifida (Q05.0–Q05.9)
- 4.3 Congenital Anomalies of the Nervous System: Microcephaly
- 4.4 Congenital Malformations of the Ear
- 4.5a Overview Congenital Heart D: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Confirmation
- 4.5b Common Truncus (Q20.0)
- 4.5c Transposition of Great Arteries (Q20.3)
- 4.5d Tetralogy of Fallot
- 4.5e Pulmonary Valve Atresia (Q22.0)
- 4.5f Tricuspid Valve Atresia (Q22.4)
- 4.5g Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (Q23.4)
- 4.5h Interrupted Aortic Arch (q25.21, Preferred; Also Q25.2, Q25.4)
- 4.6 Orofacial Clefts
- 4.7 Congenital Malformations of the Digestive System
- 4.8 Congenital Malformations of Genital Organs Hypospadias (Q54.0–Q54.9)
- 4.9a Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Talipes Equinovarus (Q66.0)
- 4.9b Congenital Malformations and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System: Limb Reduction Defects/Limb Deficiencies
- 4.9c Limb Deficiency Amelia (Q71.0, Q72.0, Q73.0)
- ›4.9d Limb Deficiency: Transverse Terminal (Q71.2, Q71.3, Q71.30, Q72.2, Q72.3, Q72.30)
- 4.9e Limb Deficiency: Transverse Intercalary (Q71.1, Q72.1, Q72.4)
- 4.9f Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Preaxial (Tibia, Radius, First Ray) (Q71.31, Q71.4, Q72.31, Q72.5)
- 4.9g Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Postaxial (Fibula, Ulna, Fifth Ray) (Q71.30, Q71.5, Q72.30, Q72.6)
- 4.9h Limb Deficiency: Longitudinal Axial Limb Deficiency – Split Hand and Foot (Q71.6, Q72.7)
- 4.10 Abdominal Wall Defects
- 4.11 Chromosomal Abnormalities